A Full Guide to AI Development Cost in 2026
How much does AI really cost in 2026? From $5K pilots to multi-million-dollar enterprise systems, this guide explains why AI budgets vary so widely and what factors matter most when planning your investment.
Contents
The growing demand for AI continues to drive up the cost of skilled talent, while infrastructure needs, from GPUs to cloud platforms, add further expenses. At the same time, evolving regulations and compliance requirements introduce new layers of complexity. These pressures make cost management a central challenge for organizations developing AI.
AI projects can vary widely in complexity, from small proof-of-concept pilots to enterprise-scale deployments that touch multiple business systems. Each stage comes with its own cost drivers, risks, and long-term commitments.
How Much Does AI Cost? Key Trends to Watch in 2026
How much does it cost to build an AI? Small projects may start at around $5,000, while enterprise-grade systems with advanced infrastructure and compliance requirements can cost several million dollars. In this section, we’ll take a look at the factors behind AI’s wide cost range, outline average benchmarks by project type, and track how budgets have shifted in recent years.
Estimated Average AI Development Cost Ranges by Project Type
AI prices vary based on multiple factors, including complexity, data requirements, and the degree of integration with enterprise systems. Here are broad ranges that reflect typical benchmarks:
Simple AI tools (e.g., chatbots, basic ML features): $5,000–$50,000
These projects are typically straightforward, with limited features and minimal integration. They’re the most affordable way to get started with AI, but the lower price often means tradeoffs in scalability, flexibility, and long-term impact.
MVPs with generative AI or integrations: $50,000–$100,000
Projects in this range usually incorporate generative AI features or multiple system integrations. The cost includes foundation models and the time required for production-ready teams.
Enterprise-grade AI solutions: $500,000+
Large-scale systems with advanced infrastructure, compliance requirements, and broad deployment across business units can exceed $500,000, often reaching into the seven-figure range.
🟢 Further Read: Can you build AI for $5K?
Why does the cost of artificial intelligence vary so widely?
AI software cost spans such a wide range because no two projects are alike. The type of AI solution, data volume and quality team size and expertise, and complexity of integrations all play a role. Compliance demands, infrastructure choices, and geographic differences in talent costs add even more variability. Together, these factors explain why budgets can range from small pilots costing tens of thousands to enterprise programs running into the millions.
How Much AI Software Costs Compared to Previous Years
In 2025, the global AI market reached over $244 billion, compared to $50 billion in 2023. The rise comes from heavier spending on computing power, generative AI, and specialized talent, all of which keep driving development budgets up. Costs for GPUs and cloud platforms, in particular, have become major drivers for projects that rely on large language models or real-time applications.
This growth isn’t slowing down, with forecasts suggesting the market could top one trillion dollars by 2031. Better automation and data tools might ease some expenses, but larger models, stricter regulations, and wider enterprise adoption mean the cost of AI will likely continue to rise.
🟢 Interested in what makes some AI solutions cost thousands while others reach millions? Check out our AI development costs breakdown
Key Factors Affecting the Cost of AI Development
AI development costs in 2026 will depend on specific, measurable drivers rather than a single fixed price. Model type, data quality, team expertise, and system integration level all drive expenses. In this section, we break down each of these factors to show how they shape your overall investment.
Type of AI and Model Complexity
The baseline cost of AI development depends largely on the chosen AI approach. Simpler, deterministic systems are more affordable to design and maintain, while advanced models require specialized technical expertise and infrastructure.
Rule-Based Systems
These rely on predefined logic and “if-then” rules. They are relatively inexpensive to build since no training data or GPUs are required. However, rule-based systems are limited in scalability and flexibility, making them suitable mainly for narrow use cases such as compliance checklists or automated workflows.
Machine Learning (ML) Models
Supervised and unsupervised ML models introduce higher costs as they require data preparation, model training, and tuning. Expenses increase depending on dataset size, experimentation cycles, and deployment environment. While some companies reduce these costs by turning to machine learning as a service (MLaaS), ML models remain a cost-efficient option for structured prediction problems like churn analysis or fraud detection.
Deep Learning and Neural Networks
Neural networks demand high-volume data, computing power, and specialized engineering expertise. Training a production-grade neural network can involve thousands of GPU hours. While expensive, deep learning is essential for high-accuracy tasks like image recognition, speech processing, or recommendation systems.
Natural Language Processing and Computer Vision
Specialized fields like NLP and computer vision often need domain-specific data labeling and advanced architectures such as transformers or CNNs. Costs increase due to the added effort of annotation, fine-tuning, and meeting compliance requirements, especially when working with sensitive data like medical text or biometric images.
Generative AI (LLMs and Agentic AI)
LLM software development and agentic AI systems are resource-intensive. Agentic AI costs include model fine-tuning or pre-trainings, access to proprietary APIs, and robust governance to avoid model drift or security vulnerabilities. While many enterprises rely on foundation models from providers, custom adaptation and compliance frameworks can push costs significantly higher.
Data and Dataset Size: Costs and Implications for the Cost of Implementing AI
Data powers every AI system, and preparing it is often the most demanding part of a project. Its scale, quality, and governance directly affect both complexity and overall costs, making it a core piece of what is required to build an AI system.
Data Collection and Preparation
Acquiring data, whether proprietary, synthetic, or third-party, incurs direct costs. Cleaning, normalizing, and augmenting datasets requires data engineering pipelines and validation processes. In regulated industries like finance or healthcare, data collection must also align with audit trails and compliance standards.
Data Labeling and Annotation
For supervised models, human-in-the-loop annotation remains one of the largest hidden costs. Advanced tooling and semi-automated pipelines reduce some of the burden, but manual quality assurance is still critical. Costs scale with dataset size, task complexity, and workforce geography.
Data Security and Privacy Compliance
Handling enterprise data is inseparable from compliance frameworks, such as GDPR, CCPA, HIPAA, or EU AI Act. Secure storage, encryption, data residency controls, and independent audits all add recurring costs. For multinational organizations, this often means building localized data pipelines to comply with regional laws.
| Activity | Key Roles | Tools & Platforms | Infrastructure Needs | Typical Cost Impact |
| Collection& Preparation | Data engineers, domain experts, data stewards | ETL tools (e.g., Apache Airflow), data wrangling libraries, synthetic data generators | Cloud storage, compute for cleaning/transforming, APIs for external data ingestion | High |
| Annotation & Labeling | Human annotators, quality reviewers, subject-matter experts | Labeling platforms (Labelbox, Scale AI), semi-automated annotation tools, crowdsourcing platforms | Scalable storage for iterative datasets, integration with MLOps pipelines | Medium – High |
| Security & Compliance | Security engineers, compliance officers, legal advisors | Governance frameworks, encryption/key management, audit logging tools, differential privacy solutions | Regionalized data centers, redundant storage, compliance monitoring systems | Medium |
🟢 Curious how to balance fast delivery and manageable risk in AI projects? See our guide to AI MVP scoping
AI Talent and Team Composition
AI development requires a combination of specialized expertise. A typical team often includes:
- AI/ML engineers. They design, build, and deploy machine learning models, ensuring they run efficiently in production environments.
- Data scientists. They explore data, build features, and run experiments to identify the most effective modeling approaches.
- MLOps specialists. Create and maintain pipelines for training, deployment, and monitoring, helping AI systems stay reliable over time.
- Data engineers. Develop the infrastructure for collecting, storing, and transforming data so it’s ready for analysis and model training.
- Domain experts. Provide subject-matter knowledge to align models with business goals and validate outputs against real-world use cases.
- Project managers. They oversee timelines, budgets, and stakeholder communication to keep the project on track.
- UX designers. They design interfaces and user flows that make AI-driven products practical and accessible for end users.
The ongoing shortage of skilled AI professionals continues to drive salaries higher, especially for hybrid roles that require cross-domain expertise. To manage generative AI costs, many companies rely on outsourcing or partnerships, though even these options can’t fully offset the premium associated with hard-to-find talent.
Technology Stack and Infrastructure Costs
Infrastructure choices have long-term cost implications and play a major role in answering what is the cost of AI for a given project:
- Cloud platforms offer scalability but can drive high operational expenses at scale (compute, storage, data transfer).
- On-premise setups require large upfront investments in GPUs/TPUs, but can provide more predictable long-term cost control.
- Hybrid approaches are increasingly common, balancing compliance needs with cloud elasticity.
The choice depends on data governance requirements, expected workload, and the need for near-real-time inference.
Integration Complexity Across Enterprise Systems
Enterprises rarely roll out AI on its own. The bigger costs often come from linking models to ERP, CRM, supply chain, and customer-facing systems. Integration requires data mapping, workflow orchestration, and security testing, all of which add time and expense. Legacy systems amplify complexity, while modern cloud and microservices architectures help reduce it.
Key cost drivers include system age and architecture, data processing, and security or compliance requirements. Real-time integrations, for example, demand low-latency infrastructure and continuous monitoring, while batch processes are more budget-friendly but less responsive.
Maintenance and Ongoing AI Software Costs
AI systems require continuous oversight to remain accurate, compliant, and cost-effective. Once deployed, models begin to drift as data changes, regulations evolve, and business requirements shift. Without active maintenance, performance degrades, risks increase, and the original investment loses value — a clear example of why AI is expensive to build and sustain over time.
Typical ongoing costs include:
- Monitoring and performance tracking — detecting accuracy drops, bias, or concept drift.
- Regular retraining with new data — updating models to reflect current realities.
- Compliance updates — adapting systems to evolving regulations such as the EU AI Act or sector-specific standards.
- Scaling and infrastructure adjustments — expanding capacity as user demand and workloads grow.
These activities often demand more resources over time than the initial build, especially in enterprise settings where uptime, auditability, and user trust are critical. Organizations that treat AI as an ongoing operational capability with a dedicated budget, processes, and staff are more likely to capture lasting value rather than facing spiraling costs or failed adoption.
🟢 Want to see how AI transforms learning experiences? Check out our article on AI personalization in education
Artificial Intelligence Cost Estimation for 2026
AI development costs can’t be represented by a single figure. They are distributed between different phases, technical resources, and long-term operations. Each stage brings distinctive priorities — from testing feasibility to scaling across the enterprise, from securing infrastructure to ensuring compliance.
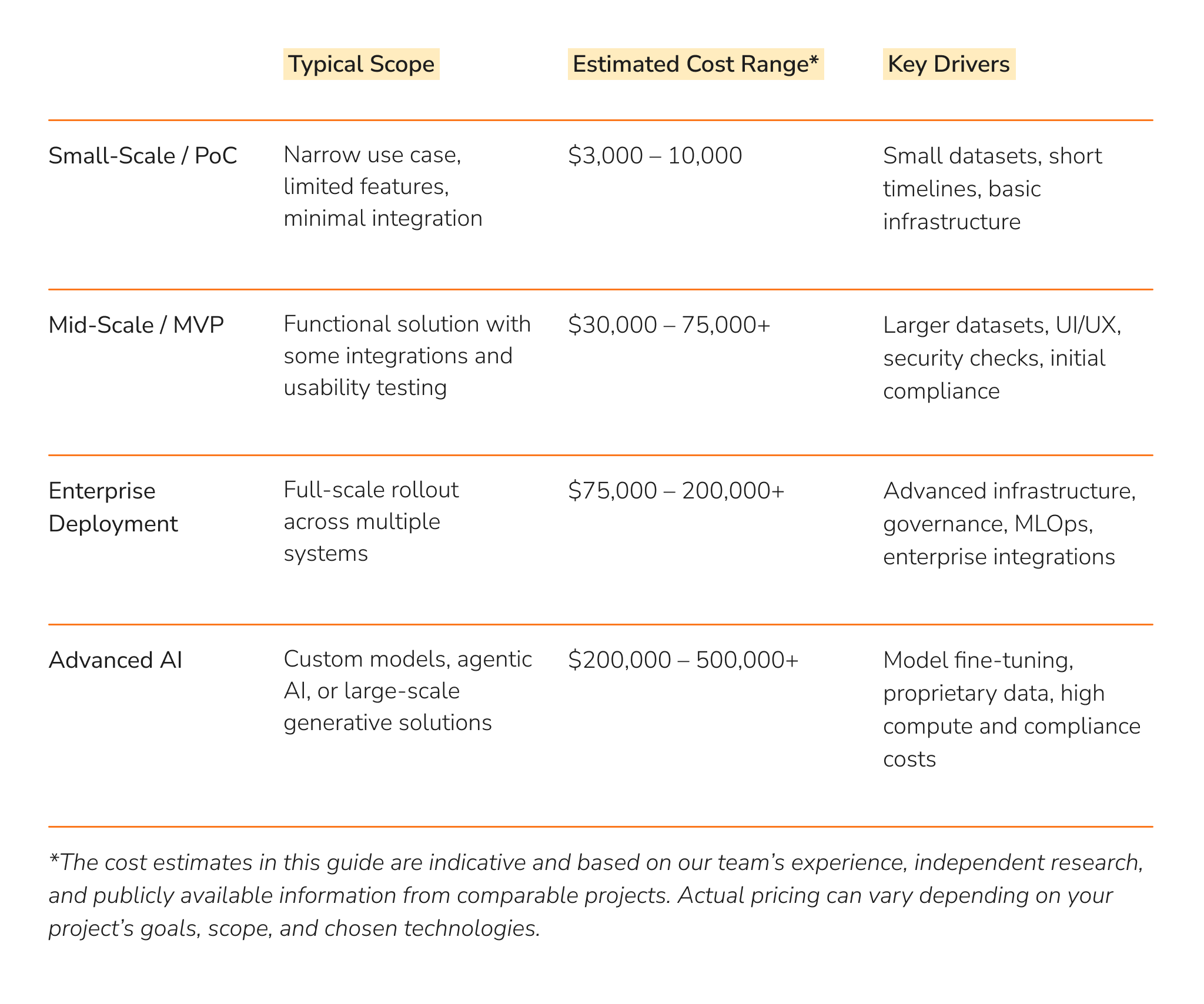
AI Prices by Project Phase
AI projects typically progress through three stages, each with its own objectives, deliverables, and budget. They start with a proof of concept to test feasibility, grow into a minimum viable product to prove usability, and eventually reach full-scale deployment where AI is integrated across the enterprise.
Proof of Concept (PoC)
A PoC validates whether an AI idea is technically feasible and capable of delivering business value. Costs remain relatively low since teams work with limited datasets, simplified models, and quick feedback cycles. Expenses still include data preparation, initial engineering, and short-term infrastructure. The main goal is to reduce uncertainty before larger investments.
Minimum Viable Product (MVP)
An MVP is built on PoC results to create a functional version of the solution. Costs increase as teams expand datasets, improve model accuracy, and build basic integrations with enterprise systems. This stage often requires UI/UX design, security reviews, and early compliance checks. The MVP helps evaluate real-world usability and refine requirements ahead of scaling.
Full-Scale Implementation
Full deployment brings AI into production systems across the enterprise. This stage requires the biggest investment, with extensive infrastructure, enterprise-grade integrations, governance, and ongoing MLOps. Costs also grow with user adoption, real-time processing, continuous monitoring, and model retraining pipelines. While resource-intensive, full-scale implementation delivers the strategic impact AI promises and serves as a clear example of how to build an AI system that achieves automation at scale, improved decision-making, and measurable ROI.
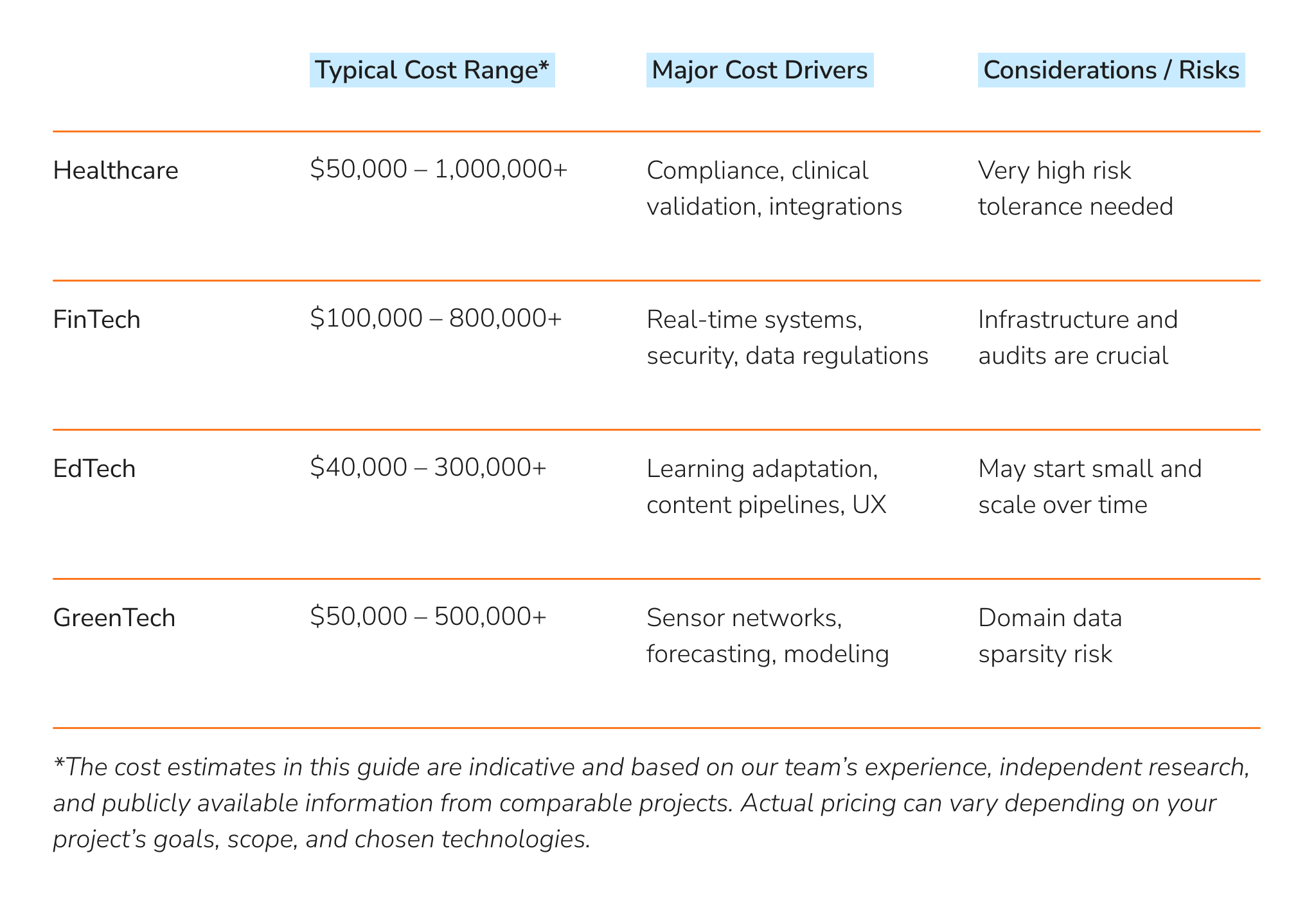
AI Development Cost by Industry
The price of AI software varies across industries. Key factors include regulatory demands, data complexity, and how deeply the system needs to integrate. Some sectors carry heavier compliance requirements, while others need more advanced data engineering or infrastructure.
Healthcare $50,000 to $1,000,000+
Healthcare AI projects handle sensitive patient data, require complex integrations with hospital systems, and must comply with strict privacy rules like HIPAA. Budgets often rise when solutions must also deliver explainability and undergo clinical validation, for example, an AI-powered medical platform that supports diagnostics or treatment planning.
FinTech $100,000 to $800,000+
AI-based FinTech applications must meet high standards for security, auditability, and compliance with regulations such as KYC or PCI DSS. Costs increase when real-time fraud detection, risk modeling, and transaction monitoring are required, as these use cases require both high-performance architecture and continuous oversight.
EdTech $40,000 to $300,000+
EdTech solutions typically focus on adaptive learning, content recommendation, or personalized tutoring. Budgets vary depending on dataset size, integration with learning management systems, and the level of UX complexity.
GreenTech $50,000 to $500,000+
GreenTech projects often rely on IoT sensors, predictive models, and environmental simulations. Costs increase when domain-specific modeling and hardware integration are required, for example, an AI-powered system for a greentech provider that forecasts energy demand or monitors emissions.
Hidden Costs of Artificial Intelligence
- Data storage and transfer. Ongoing fees for cloud storage, backups, and bandwidth as datasets grow.
- Model retraining. Regular updates required to maintain accuracy and avoid performance drift.
- Compliance and audits. Expenses related to evolving regulations, certifications, and third-party assessments.
- Integration upkeep. API maintenance and adjustments when connected systems are updated.
- User training and change management. Time and resources to help employees adopt AI solutions effectively.
- Support and incident response. Addressing system downtime, errors, or unexpected behaviors in production.
🟢 Want to see how virtual assistants help reduce waste and optimize energy? Explore our GreenTech AI chatbot guide
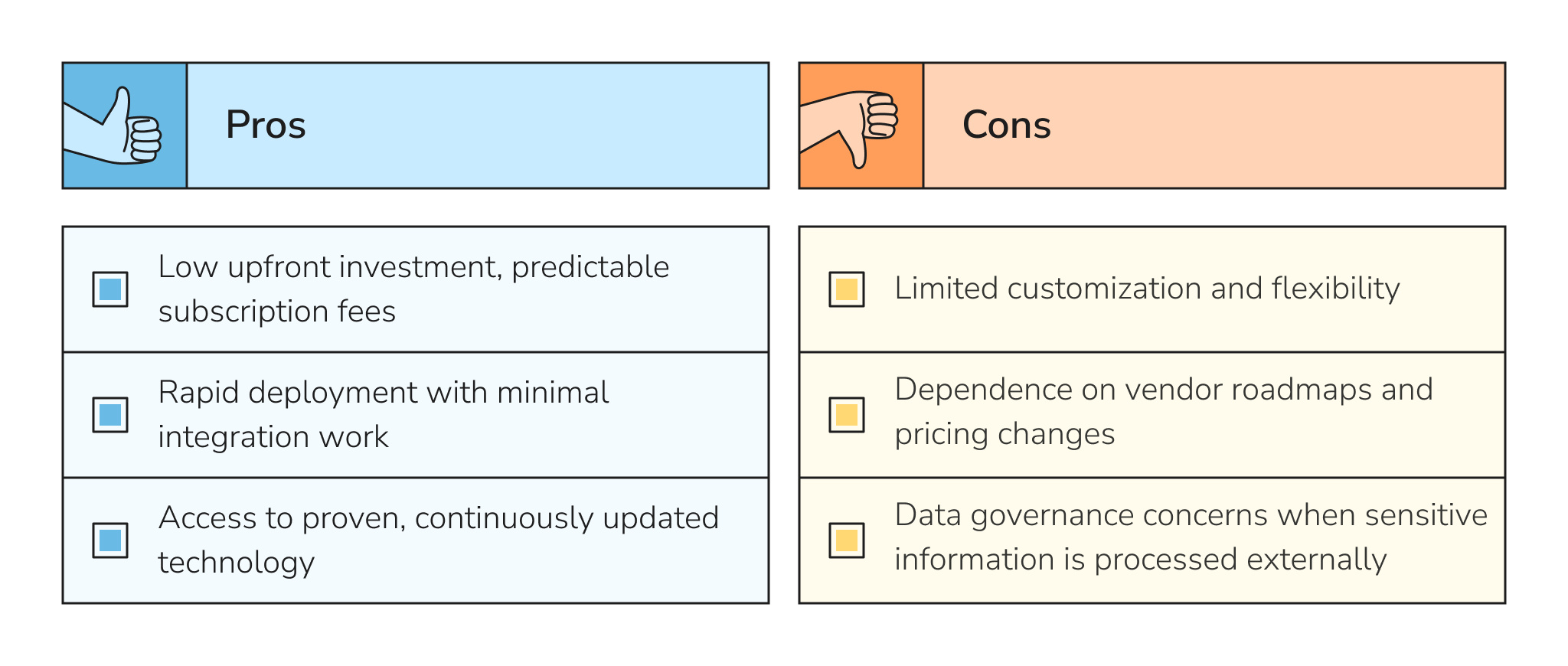
Custom AI Development vs. Off-the-Shelf AI Software
When starting an AI project, one of the first strategic decisions is whether to use pre-built software or invest in custom development. Off-the-shelf platforms and ready-made APIs offer a quick, affordable way to test AI capabilities but are limited in flexibility, data control, and long-term scalability. Custom development costs more upfront and takes longer, but it gives companies the ability to shape solutions around their workflows, protect sensitive data, and build unique value.
Pre-Built AI Software Prices and Ready-Made APIs
Pre-built AI platforms and APIs, such as speech-to-text, translation, or sentiment analysis services, offer a fast, low-cost entry point. Pricing models are usually subscription-based or pay-per-use, starting as low as a few cents per API call and scaling into thousands of dollars monthly for enterprise usage.
Custom AI Development Costs
Custom AI solutions are designed to meet specific business requirements. Budgets typically range from $70,000 for smaller projects to several million dollars for large-scale enterprise deployments. The investment is higher, but so is the potential to create proprietary value.

In-House vs. Outsourcing AI Development: What Is the Cost Difference?
Deciding between in-house development and outsourcing has a direct impact on both cost and flexibility. An in-house team provides more control and alignment but requires continuous investment in talent, infrastructure, and training. Outsourcing or nearshoring reduces overhead and offers access to specialized expertise, but may introduce dependency on external partners.
- In-House Development: Higher fixed costs (salaries, benefits, infrastructure) but potentially lower variable costs when projects are ongoing.
- Outsourcing / Nearshoring: Lower upfront costs, faster access to niche expertise, and scalable engagement models. Overall cost efficiency depends on the choice of a development partner and long-term governance.
Companies often find the optimal strategy in a hybrid model: maintaining a core internal AI capability while partnering with external experts for specialized needs. This approach balances long-term control, flexibility, and cost efficiency.
🟢 Exploring your chatbot development options? Read our comparison guide on custom-build and pre-configured chatbot solutions
Artificial Intelligence Pricing Models in 2026
The structure of a development contract influences not only the budget but also shapes flexibility, risk, and long-term deliverables. Companies typically choose from three main pricing models: fixed price, time and materials, or dedicated teams.
Fixed Price Model for AI Projects
A fixed price model sets the scope, timeline, and budget upfront. This approach works best for projects with well-specified requirements and a simple structure. While it provides financial predictability, this cooperation model leaves little room for iteration — a potential drawback when data quality or technical feasibility changes during the project.
Time and Materials (T&M) Model
The T&M model bills for actual time spent and resources used. It provides flexibility for experimentation, making it suitable for projects where requirements evolve as data insights emerge. The downside is less predictability: costs can increase if teams need more time to achieve target performance or additional system integrations.
Dedicated Team Model
In this setup, a company hires a team of AI specialists who work as an extension of its in-house staff. The dedicated team model offers scalability, continuity, and knowledge retention, making it ideal for long-term or large-scale AI initiatives. The ongoing commitment, however, requires organizations to allocate steady budgets and active governance to maintain efficiency over time.
How do different pricing models shape the cost of AI development? The optimal pricing model depends on the project stage, clarity of scope, and organizational priorities. Fixed price works well for small, low-risk pilots. Time and materials fit better for exploratory projects that need flexibility. Dedicated teams make the most sense when a company views AI as a long-term capability, not a one-off project.

🟢 Want to help your team get the most out of ChatGPT? Read our article ChatGPT for Tech Teams: Tips for a Team Leader
How to reduce the cost of implementing AI in 2026?
- Start with a clear AI strategy. Projects that begin without a well-defined purpose often burn through resources before delivering value. A well-structured strategy aligns technical choices with business goals, sets measurable success metrics, and keeps teams focused on high-impact features.
- Leverage pre-trained models and open-source tools. Developing models from scratch can be resource-heavy. Pre-trained models and open-source frameworks provide a strong starting point, cut down on data needs, compute requirements, and development time. This approach allows teams to focus on customization and integration rather than rebuilding proven components.
- Optimize data preparation and annotation. Data work often represents the largest hidden cost in AI development. Establishing efficient pipelines, using semi-automated labeling tools, and applying consistent quality checks early on can reduce waste and speed up later stages of development. Strong data foundations also prevent costly rework down the line.
- Choose the right cloud infrastructure. Cloud platforms make scaling easier, but costs can rise fast if usage isn’t optimized. Matching workloads to the right pricing models, balancing on-demand services with reserved instances, and monitoring usage closely can yield significant project cost savings.
- Consider nearshoring or outsourcing. Partnering with skilled AI teams in cost-effective regions allows companies to balance expertise and budget. Nearshoring offers better timezone alignment and smoother collaboration than offshoring, while still helping enterprises reduce overhead compared to hiring in high-cost markets.
🟢 Curious how AI chatbots are becoming a core business tool? Read our guide AI Chatbots for Business: The Essential Tool
ROI of Artificial Intelligence Development
Measuring the return on investment from AI initiatives is just as important as understanding their costs. While budgets can be extensive, effective AI systems often generate value that far outweighs the initial spend. This value may take the form of efficiency gains, new revenue streams, improved compliance, faster product cycles, or stronger customer experiences. As such, ROI has to be considered both in financial and non-financial terms.
Realizing ROI takes planning and clear metrics. Companies that set success criteria early, track results, and adjust as models evolve are more likely to sustain long-term value. ROI varies by industry — automation in logistics differs from predictive analytics in healthcare.
Key areas where AI creates ROI include:
- Process efficiency and automation. Reducing manual tasks, accelerating workflows, and lowering operational costs.
- Revenue growth. Enabling new products, services, or personalization strategies that expand market opportunities.
- Risk reduction. Improving fraud detection, compliance monitoring, and predictive maintenance to minimize the exposure.
- Decision-making quality. Providing insights that help leaders act faster and with greater accuracy.
- Customer experience. Powering chatbots, recommendation engines, and personalization features that drive retention and satisfaction.
- Innovation enablement. Opening new business models or capabilities that would not be feasible without AI.
Continuous monitoring, retraining, and alignment with evolving business goals ensure that systems remain relevant and effective over time. Companies that embed AI into core operations, rather than limiting it to experiments, are more likely to see compounding returns in a viable future.
🟢 Looking for real examples of AI agents driving impact beyond efficiency? Dive into AI Agents & the Future of Corporate Sustainability
How Beetroot Helps with AI Development Cost Management
Managing AI app development cost isn’t only about cutting expenses, it’s about aligning investment with lasting value. At Beetroot, we act as a scalable partner, combining domain expertise with a focus on sustainability across every project. By tailoring cooperation models and team composition, we help organizations manage costs responsibly while keeping projects on track for tangible impact.
Our services cover the full AI lifecycle, including:
- AI software development services: End-to-end support from idea validation to enterprise deployment.
- Generative AI consulting services: Consulting and implementation support to adapt large language models for specific business needs, from content generation to workflow automation.
- Natural language processing services: Building systems that understand, analyze, and generate text.
- Agentic AI development services: Developing autonomous agents that handle multi-step reasoning and tasks.
- MLOps consulting services: Consulting to set up pipelines that keep AI models reliable, scalable, and cost-efficient.
- AI chatbot consulting: Consulting to design and build conversational tools that improve customer and employee interactions.
Combined, this expertise allows us to help companies balance innovation with cost efficiency and ensure that AI investments deliver sustainable results over time.
Planning Your AI Budget with Confidence
AI development costs can vary widely, but understanding the key drivers makes it easier to plan strategically and invest where it matters most. Whether you’re exploring a proof of concept, preparing an MVP, or scaling to enterprise deployment, careful cost management is essential to achieving long-term ROI.
Looking for tailored guidance on budgeting and implementation? Contact us to discuss your AI initiatives and explore how our team can support your next steps.
🟢 DOWNLOAD NOW: AI Development Cost Checklist (PDF)
FAQs
How do mid-sized companies and enterprises typically budget for AI development costs?
Organizations usually allocate AI budgets in phases: proof of concept, MVP, and full-scale deployment. Early phases are often funded as innovation initiatives, while later stages shift into core IT or digital transformation budgets. Enterprises also budget for ongoing operations like monitoring, retraining, and compliance, which can cost more than the initial build. To handle uncertainty in data, integrations, and talent, many companies use scenario-based budgeting, planning for best case, expected, and high-risk ranges.
How does team composition impact total AI builder cost?
Team composition drives one of the largest portions of AI budgets. Highly specialized roles such as ML engineers, data scientists, and MLOps specialists command premium salaries, especially in regions where AI talent is scarce. Small projects may need a couple of experts when larger initiatives require cross-functional groups.
How do developing an AI model from scratch and using pre-trained models/APIs compare in costs for 2026?
Building from scratch typically requires large datasets, specialized infrastructure, and highly skilled teams, resulting in higher upfront costs but greater customization. Pre-trained models or APIs make it easier to get started by cutting down on data and compute needs. They let companies build solutions faster and cheaper, but they also bring ongoing fees and the risk of vendor lock-in. The choice comes down to goals: businesses looking for unique differentiation often invest in custom models, while those focused on speed and savings turn to pre-trained options.
How do AI development costs differ based on location (e.g., US vs. Europe vs. Asia)?
Hiring AI developers in the US and Western Europe typically comes at a higher cost due to competitive salaries and stricter compliance environments. Eastern Europe and parts of Asia (for example, Vietnam) often provide more cost-effective engineering talent without sacrificing quality, though cultural and time-zone differences may require additional management overhead. Enterprises with global presence sometimes adopt a hybrid approach, leveraging nearshore or offshore talent for engineering tasks while keeping governance and compliance close to headquarters.
How much does artificial intelligence cost after implementation?
Ongoing expenses often surpass initial development. These include infrastructure costs for cloud or on-premise environments, regular retraining with new data, continuous monitoring for accuracy and bias, and updates to align with evolving regulations. Support costs also grow as adoption increases, requiring scaling of APIs, GPUs or integration pipelines. Enterprises should plan for MLOps teams or service providers to manage these activities. Treating AI as an operational capability, rather than a one-time project, is essential to sustain value and avoid performance decline.
How do AI pricing models affect the overall cost of artificial intelligence?
Pricing models shape cost predictability and flexibility. Fixed price contracts provide budget certainty but work best for well-defined projects with limited scope. Time and materials models gives room to iteration and adaptation but can increase in cost if timelines stretch. Dedicated team models suit enterprises building long-term AI capability, offering continuity and scalability at the expense of ongoing budget commitments. Choosing the right pricing model depends on project maturity, risk tolerance, and whether the organization views AI as an experiment or a strategic capability.
How much does compliance and regulation add to AI development cost in 2026?
Compliance costs vary by industry and geography but can represent a significant portion of budgets. Healthcare, finance, and government projects face stricter requirements and add expenses for secure infrastructure, audit trails, explainability, and data residency. Regulations such as the EU AI Act and updated data privacy laws drive investment in legal review, documentation, and monitoring. While compliance adds upfront and recurring costs, neglecting it risks fines, reputational damage, and project failure. Enterprises increasingly treat compliance not as an add-on but as a core cost driver in AI projects.
What is the best way to link AI cost to ROI for enterprise organizations?
Enterprises can compare AI costs with outcomes like efficiency gains, fewer errors, or new revenue streams. It starts with clear KPIs at the PoC stage and continues through the MVP and full rollout. While upfront costs may be high, such long-term benefits as automation, better decisions, and faster workflows often deliver strong returns. Factoring in avoided costs, such as fines or manual labor, gives a fuller picture of AI’s financial impact.
What are the most effective ways to reduce AI development costs without sacrificing quality?
Companies can control costs by reusing pre-trained models, leveraging open-source frameworks, and focusing on high-value use cases rather than broad, unfocused projects. Data prep usually takes the most resources, so fixing pipelines early saves time and money later. Working with experienced vendors or outsourcing certain roles can ease budget pressure while keeping access to expertise. Investing in MLOps also cuts long-term costs by streamlining model management and reducing retraining needs.
How long does it typically take to develop and deploy an AI solution?
A proof of concept can take a few weeks while an MVP often requires three to six months. Full-scale deployments can stretch past a year when large datasets, complex integrations, or compliance demands are involved. Data readiness, infrastructure, and stakeholder alignment all influence speed, which is why phased approaches work best because they deliver value early while longer initiatives move forward.
How can I get an accurate cost of generative AI for my specific project idea?
Getting an accurate estimate means matching technical needs with business goals. Most projects start with a discovery workshop to review data readiness, integration challenges, compliance, and success criteria. From there, teams can outline cost scenarios by phase and risk. Online calculators may give a rough idea, but they often miss enterprise-level complexity. Working with experienced AI partners helps refine estimates and strike the right balance between scope, budget, and outcomes before making big investments.