How to Run a Website Accessibility Audit: A Digital Agency’s Guide
Contents
- Understanding Web Accessibility for Digital Agencies
- Preparing for a Website Accessibility Audit
- Conducting a Website Accessibility Audit
- Documenting Findings and Reporting
- Remediation and Implementation
- Web Accessibility Testing and Validation
- Promoting a Culture of Accessibility
- Building Digital Products That Work for Everyone Together
Contents
- Understanding Web Accessibility for Digital Agencies
- Preparing for a Website Accessibility Audit
- Conducting a Website Accessibility Audit
- Documenting Findings and Reporting
- Remediation and Implementation
- Web Accessibility Testing and Validation
- Promoting a Culture of Accessibility
- Building Digital Products That Work for Everyone Together
According to 2022 data from World Health Organization, there is an estimated 1.3 billion people worldwide experiencing significant disability. Yet, as of 2022, only around 3% of the internet can be called completely accessible, with many business owners not even knowing they have to make their digital platforms equally inclusive to every user out there.
For digital agencies developing multiple websites and apps for their clients, the benefits of web accessibility are worth the investments it requires. Companies dedicated to building accessible platforms can enlarge their database, mitigate legal risks, enhance search engine optimization, and more. However, we at Beetroot suggest prioritizing another advantage above all else, and that is an equally satisfying experience for everyone.
Our team regularly organizes educational events to share tips and tricks on building better products. Recently, Beetroot’s WordPress developer Maksym Kalashnykov spoke at an online event on how to do a website accessibility audit and why it is important. Based on his lecture, we’ve created this guide on website accessibility audits and what they can give your digital agency in the long run.
Understanding Web Accessibility for Digital Agencies
In his lecture, Maksym Kalashnykov mentions two reasons businesses usually care about web accessibility:
“The first reason is providing equal opportunities to people with and without disabilities. The second one is avoiding an expensive lawsuit since different countries have different regulations regarding web accessibility. I strongly suggest you stick to the first reason: equal opportunities.”
So, let’s explore why this argument should indeed be a priority.
What is Web Accessibility?
Web accessibility is the practice of designing and developing digital products, like websites and mobile apps, in a way that allows people with disabilities, impairments, and limitations to perceive, understand, navigate, and interact with a given digital product effectively. In other words, it ensures that users with visual, auditory, cognitive, motor, or other disabilities can access and use online information and services without barriers.
As a rule, it is achieved by following standards and guidelines such as the Web Content Accessibility Guidelines (WCAG) issued by the World Wide Web Consortium (W3C). These standards include providing alternative text for images and captions for multimedia content, using clear and well-structured content, implementing navigational elements accessible via keyboard, ensuring readability through color contrast, and more.
Benefits of Following Web Accessibility Guidelines for Digital Agencies
When managing dozens of software products for different clients, it might be challenging to make web accessibility a priority and ensure all the platforms comply with relevant guidelines. However, it is worth the effort for digital agencies striving for excellence. After all, consistent commitment to web accessibility directly influences the agency’s reputation, which inevitably impacts its trustworthiness, increasing client satisfaction and retention.
Moreover, building accessible digital products helps digital agencies reach a broader audience, and by this, we don’t just mean people with disabilities. In Beetroot’s experience, software products that follow web accessibility guidelines provide a better user experience and improved usability and increase audience reach.
Video captions are helpful not just for people with hearing impairments but for non-native speakers. Clear, readable content means users in challenging environments can access it. Older adults who experience age-related visual or motor impairments will appreciate features like larger text, clear contrast, web color accessibility, and easy-to-use navigation. The list of examples of web accessibility benefiting everyone goes on.
Accessibility Web Standards and Legal Responsibilities
Many countries have laws and regulations requiring websites to be accessible. For instance, the US has the Americans with Disabilities Act, and the European Union controls it through Web Accessibility Directive.
Recently, the amount of lawsuits regarding website accessibility has been rapidly increasing. In the US, the number of lawsuits filed in federal courts increased between 12 and 14% annually between 2019 and 2022. Most of such lawsuits are caused by people with disabilities being unable to access and use web platforms effectively. Even big corporations often fail to deliver accessible software: in 2019, the court found Domino’s Pizza violated the ADA by having an inaccessible website.
When building web products for their clients, digital agencies must ensure they comply with relevant web accessibility laws and regulations. That is why we at Beetroot always recommend taking a proactive approach to addressing accessibility barriers in order to mitigate legal risks and potential penalties.
Preparing for a Website Accessibility Audit
Researchers involved in a 2021 study by WebAIM analyzed the home pages of the top million websites and detected over 51 million distinct accessibility errors. This means an average of 51.4 errors per home page.
If you don’t want the products you develop for your clients to end up on the list of websites that fail to be inclusive, it’s essential to conduct website accessibility audits. Here is a list of steps digital agencies and development teams need to take before conducting such inspections.
Educating the Team
How to test web accessibility? What are the main inclusivity guidelines a development team needs to follow? And why is web accessibility important in general? To build a truly accessible digital product, every person on the team must know the answers to these questions and be on board with achieving accessibility. This includes everyone, from UI/UX designers and developers to the stakeholders. Therefore, it’s essential to conduct regular educational events on accessible design principles, coding techniques, and other training workshops.
In case your in-house team doesn’t have sufficient web accessibility experience, you can also engage external experts to consult your specialists on the matter and provide guidance throughout the audit process.
Establishing Accessibility Guidelines
The next step in this journey is making sure the whole team is familiar with the specific accessibility guidelines or standards that will be used in the website accessibility audit. For instance, the most common directive for UI/UX designers and software developers is the WCAG audit based on the global standards developed by the World Wide Web Consortium (W3C).
Following WCAG 2.0 standards, you can decide on the desired compliance level and scope and prioritize accessibility features accordingly. For instance, there are three levels of WCAG compliance: A, AA, and AAA, with the latter one representing the highest standard of accessibility.
The AA conformance level is considered to be completely acceptable since it entails comprehensive accessibility guidelines for web content, including perceivability, operability, understandability, and compatibility.
Identifying Audit Tools and Resources
The last thing to do in the preparation process is to explore and pick the website accessibility audit tools and resources for the team to use. To do so, we recommend studying global and local government guidelines and recommendations from reputable organizations, especially ones that offer web accessibility certification. Our consultant Maksym also suggests utilizing different automation evaluation tools instead of sticking to just one of those. In his lecture, he mentions WebAIM’s WAVE and Lighthouse, which is integrated into the Chrome DevTools.
It’s important to remember that automation evaluation tools are not enough for building 100% accessible digital products. The team needs to engage with the web accessibility community, seek the expertise of professionals with relevant experience, and above all, communicate with real people with disabilities who can provide honest feedback.
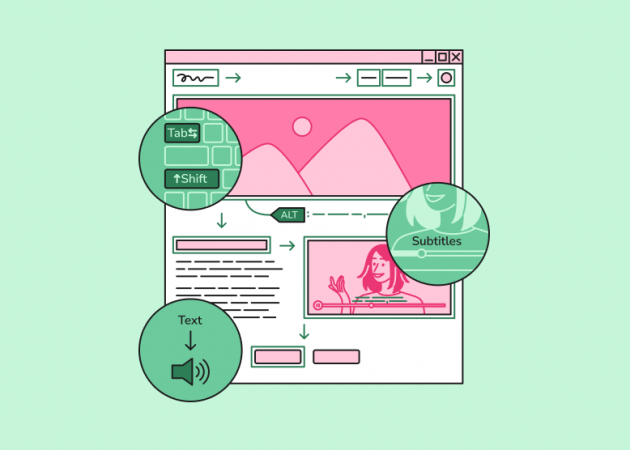
Conducting a Website Accessibility Audit
We’ve made a checklist of key accessibility aspects the development team has to pay extra attention to when building an inclusive digital platform.
- Evaluating website structure and navigation, which involves an examination of the navigation menus, site architecture, and logical content flow to ensure they are intuitive and accessible for all users, including those who rely on assistive technologies;
- Assessing color contrast, typography, and readability, which involves evaluating the color contrast between text and background elements, as well as the legibility of typography, to ensure high readability for individuals with visual impairments;
- Testing keyboard accessibility and focus management, during which the team tests whether the users would be able to effectively navigate and interact with the platform by only using a keyboard;
- Checking headings and semantic markup since they play a crucial role in providing structure and context to content published on the platform. During this step, the team reviews the use of proper heading hierarchy, semantic markups like HTML5 elements, and associations between labels and form inputs;
- Verifying multimedia accessibility, which means the team needs to ensure the presence of alt text for images, captions, and transcripts for videos, descriptions for audio content, and so on;
- Reviewing forms and interactive elements, during which the team examines form fields, labels, error messages, and other components to ensure they are accessible and easily perceivable to individuals with disabilities.
By following these steps, digital agencies and their development teams can create inclusive products that comply with web accessibility standards and serve all users better.
Documenting Findings and Reporting
Documentation of the website accessibility audit process and post-audit reports help communicate accessibility issues to stakeholders and development teams, ensuring everyone is aware of the issues that must be addressed. They also become evidence of products’ compliance with accessibility standards that can be shared with clients, investors, regulatory bodies, etc. So, here are the steps we recommend taking after you’ve conducted the audit.
Creating a Comprehensive Website Accessibility Audit Report
The web accessibility report typically should summarize all the findings and observations found during the audit and include information about the evaluated elements supported by screenshots and other types of evidence to support the findings. Additionally, the report should include the scope and methodology used during the inspection and highlight the product’s compliance with accessibility standards or regulations, such as WCAG.
Prioritizing Accessibility Issues That Need to be Addressed
After studying the audit report, the team can move on to categorizing the identified accessibility issues in web design, code, and other project aspects based on their severity, impact on inclusive user experience, and compliance with accessibility regulations. This helps understand which issues need to be immediately resolved and which can be addressed later on, thus helping the agency allocate the resources more effectively, including web design for small businesses.
Defining Clear Actionable Recommendations
One of the end goals of website accessibility audits is to create a set of relevant recommendations which may cover code changes, design improvements, content updates, interaction patterns, and other modifications. Based on these recommendations and their priority levels, the team can develop a strategy to address the issues and apply best accessibility practices.
Remediation and Implementation
Implementing the remediation strategy requires the whole team of designers, developers, QA engineers, and content creators to join forces and collaborate for the sake of efficient improvements.
For instance, engaging the design and development teams in the communication process simultaneously helps ensure they understand accessibility requirements and can successfully implement them in synergy. Such collaboration sessions include discussing audit findings and working out the solutions to solve the issues discovered.
Remediation involves making code, design, content, and other changes that will help improve the accessibility level of the product. Some of the most common adjustments include:
- enhancing color and text contrast (in fact, it is the most commonly-detected accessibility issue according to WebAIM)
- adding alternative text and image descriptions
- improving keyboard accessibility
- modifying the content structure
- providing captions and transcripts,
- implementing proper validation techniques and error messaging
- enabling skip links
Additionally, the remediation process entails the implementation of ARIA (Accessible Rich Internet Applications) attributes. Simply put, this is a set of HTML attributes that provide additional information to assistive technologies like screen readers, allowing them to better understand and interact with dynamic web content.
To give you an example, think of a website with different tabs for information structuring. With ARIA attributes, screen readers can understand and announce the selected tab’s label and associated content. Basically, it’s like using labels on folders in a filing cabinet to find and access information easily, even if you’re using assistive technologies.
When implementing fixes, it’s crucial to follow the recommendations provided in the website accessibility audit report and utilize best practices in the industry to resolve the issues and reach accessibility standards.
Web Accessibility Testing and Validation
After implementing changes, the team needs to comprehensively evaluate the product and identify any barriers they might have missed before. The testing and validation phase typically consists of the following steps.
Utilizing automated web accessibility testing tools
Testing with assistive technologies such as screen readers, magnifiers, or keyboard-only navigation tools is conducted to verify the effectiveness of the implemented solutions and ensure individuals with and without disabilities will have an equally full experience. Automated testing tools can scan the website or digital product and analyze HTML structure, CSS, and other elements to detect possible violations of accessibility standards.
Conducting manual testing with assistive technologies
Manual testing follows automated one to identify any issues automated tools may have missed, which is especially important when dealing with complex interactive components and dynamic content.
Engaging users with disabilities for feedback
No matter how many automation tools for accessibility evaluation you use, feedback from real target users with different disabilities and impairments can provide you with invaluable insights on making the product even more inclusive. Make the focus group as diverse as possible and ask the users to report on any accessibility barriers and usability challenges they encounter.
Promoting a Culture of Accessibility
Digital agencies following accessibility guidelines ensure their clients are happy with the end results. However, when accessibility is perceived as something more than just a set of obligatory rules, it can give your company much more than customer satisfaction.
Agencies that nurture a commitment to accessibility within their teams are more likely to build a positive reputation, attract clients who are seeking to build meaningful products, and get access to niche markets like government entities, inclusive and socially responsible businesses, etc. To top that, making accessibility a core aspect of the agency’s work can foster a collaborative and more inclusive work environment that leads to effective communication between different specialists and, thus, better business results.
So, how can a digital agency promote a culture of accessibility within its teams? Here are a couple of tips that can help with that.
Training agency teams on best practices
The first step in promoting web accessibility starts with providing comprehensive training to the digital agency team, where all specialists involved can explore accessibility principles, guidelines, and best practices. Such training sessions can include lectures, workshops, panel discussions, co-creation sessions, and other educational events that involve experts on accessibility. As a result, an agency can build a team empowered by knowledge and the ability to integrate accessibility principles into their daily work.
Committing to accessibility within the company
Educational programs for employees won’t work unless your digital agency is by itself an example to follow. Ensure that your own web and mobile platforms are accessible to every user out there. That’s exactly what Maksym did in his lecture: he conducted an online web accessibility check on Beetroot’s site, not just a random platform.
Advocating for inclusive design and user experience
An important part of embracing accessibility is advocating for it whenever possible, even during client interactions and project discussions. Don’t be afraid to take the initiative and educate clients and business partners about the benefits of inclusive design and the importance of web accessibility. You have the power to make inclusivity a standard requirement in all the projects your team works on.
Building Digital Products That Work for Everyone Together
For digital agencies, it might be challenging, both in terms of efforts and finances, to keep an eye on the web accessibility aspect of all the software projects they have in production. However, taking that extra mile and committing to inclusive digital experiences is worth it. Why? Well, because web accessibility makes the user journey enjoyable for everyone, regardless of the person’s abilities, disabilities, and diverse needs.
Besides, turning to a trusted outsourcing software development company with experience in building accessible web platforms can help you significantly cut costs while still delivering excellent results. So, if you are looking for a socially responsible tech partner to build inclusive digital products for your clients — Beetroot is here for you. Feel free to reach out and explore how we can create accessible platforms that work for every user.
Subscribe to blog updates
Get the best new articles in your inbox. Get the lastest content first.
Recent articles from our magazine
Contact Us
Find out how we can help extend your tech team for sustainable growth.