GreenTech, CleanTech, or ClimateTech Software Development: Decoding the Difference
Contents
Contents
Before we explore the distinctions between green, clean, and climate technologies and the role of green tech software solutions in fostering sustainability, let’s first reflect on why this topic is so important today.
In September 2023, scientists at the Stockholm Resilience Centre introduced the concept of nine planetary boundaries that outline a safe operating space for humankind. Alarmingly, six of these boundaries have already been crossed, including global warming, deforestation, and pollution of freshwater and nitrogen cycles. Crossing these limits risks triggering massive and abrupt changes in Earth’s biophysical systems, potentially starting irreversible processes that endanger the very survival of our ecosystems.
We’ve long passed the point where we could claim our actions have no environmental impact. The effects of human activity on our planet are increasingly visible daily. As this article is being written, the temperature outside stands at a sweltering 36°C as another abnormal heat wave is approaching Europe. Technology is undoubtedly only a part of the comprehensive solution to the climate crisis on a global scale, but we need it to strategize, analyze, and plan our next steps. Let’s begin by
Defining the GreenTech, CleanTech, and Climate technology
Understanding green technology
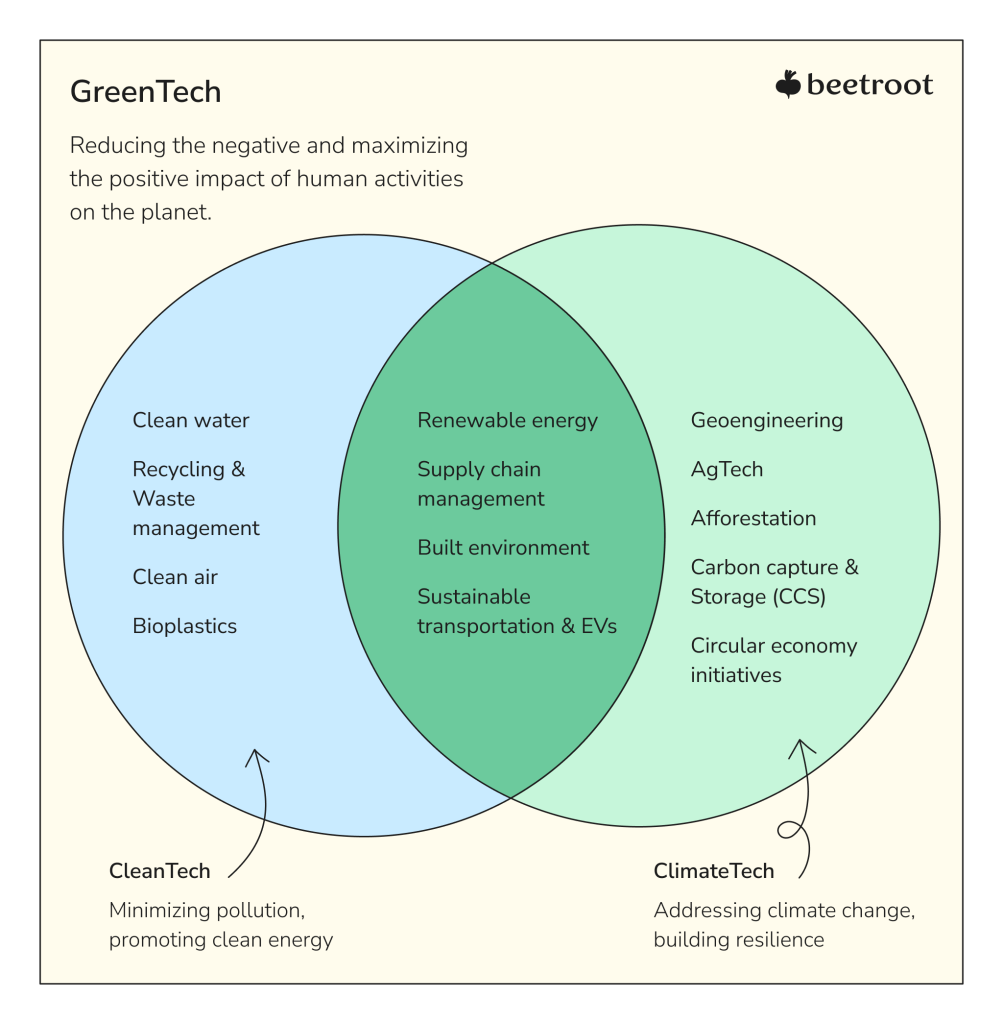
The term “GreenTech,” or “green technology,” became a namesake for any innovative technology that aims to improve sustainability or is considered sustainable based on its supply chain or production process, with “green” emphasizing its environmental benefits. GreenTech spans a wide range of industries and is generally used as a collective term for clean and climate technologies, so let’s tell the difference between these labels.
What is CleanTech?
In a nutshell, a set of technologies that contribute to improving the quality of polluted natural resources and care for the environment are dubbed as “clean,” hence the shorter term CleanTech. They focus on decarbonization by promoting environmentally friendly alternatives to traditional energy sources, materials, and building methods, aiming to reduce the negative impacts of their byproducts on the planet and biodiversity. Common examples of clean technologies include renewable energy (like solar, wind, tidal power, and biofuels), electric vehicles, waste management and recycling, combating water and air pollution, and the development of bioplastics.
Amidst growing awareness of climate change, energy security concerns, and market volatility caused by the far-reaching consequences of Russia’s war against Ukraine, global spending on low-carbon technologies increased by 17% in 2023. The segments that currently attract the most investment are renewable energy and electric transportation. Each received over US $600 billion in 2023, representing nearly three-quarters of the global energy transition spending.
What about ClimateTech?
The term “climate technology” (or “climate change technology”), shortened to ClimateTech, refers to technologies that directly address or mitigate problems associated with climate change. With the scientific evidence that this process is inevitable and irreversible, humanity can still learn to adapt to and live with the environmental changes already set in motion.
Between the two terms, “CleanTech” and “ClimateTech,” the latter has a more narrow scope. That said, while CleanTech aims to address a wider range of environmental challenges across various industries, ClimateTech focuses on the climate crisis and involves developing solutions to reduce greenhouse gas emissions, like carbon capture and storage systems, climate modeling and prediction tools, building smart grids and climate-resilient infrastructure, and helping businesses and communities adjust to climate change. The ClimateTech market is projected to grow to US $182.5 billion by 2033, despite some negative trends in venture capital investment in 2022-2023.
Under the umbrella of green technologies, CleanTech and ClimateTech overlap in sectors like renewable energy, supply chain management, the built environment, and sustainable transportation.
The role of software technology in green transformation
Similarly to how digital transformation propels businesses towards the future, software technology supports climate action to ensure this future is sustainable. A study by Accenture revealed that 92% of firms have set their sights on achieving net zero emissions by 2030, which will require deploying advanced technologies to quantify, minimize, and offset an organization’s carbon footprint and optimize operations.
From data collection and analysis to facilitating the manufacture of clean energy, software advancements are instrumental in reducing the environmental damage stemming from human activities and accelerating the transition towards renewable sources, sustainable materials, and innovation in environmental technology. The following key points illustrate how cutting-edge digital technologies endorse green innovation:
- Technology is the vital enabler of scalability;
- New software is helping make renewable energy more accessible;
- Custom software solutions improve the industry dynamics;
- Technological advancements reduce fossil fuel consumption;
- Software suites for green energy traders facilitate more profitable trades;
- Transparency in managing operations enables higher grid stability;
- Pivoting to a carbon-neutral world is possible by utilizing many existing technologies.
Emerging software technologies for CleanTech and ClimateTech solutions
Artificial intelligence
As AI, a driving force in the tech world, continues to thrive, both large-scale companies with massive ecological impressions and innovative startups increasingly leverage its potential to create more impact. With advancements in big data, hardware, and GenAI algorithms, AI plays a vital role in automating high-level processes and improving energy efficiency and environmental footprint. Below are some business cases of how AI can transform the GreenTech sector:
| Automated decision-making | Preventive maintenance of PV plants; Aided AI systems for environmental impact assessment for solar and wind sites; Eliminating human error and bias in decision-making for responsible business practices |
| Risk and opportunity analysis | Image recognition and algorithms to identify risks and opportunities for potential projects; Project modeling automation to identify profitable projects; Algorithms to create preliminary cash-flow models |
| Supply and flow management | AI/ML utilization by energy companies and grid operators to forecast generation, schedule maintenance, and manage power flows; Informing consumers about supply to help manage their consumption, distributed generation and storage, and reduce energy bills; AI algorithms to analyze smart meter data to predict demand and network load |
| Predictive maintenance systems | Predictions for short-term power output based on weather data; Energy forecasting to maintain grid stability and dispatching, streamline the plant availability, and schedule maintenance |
| Smarter economics | Applying AI to combine ML weather models, historical datasets, and real-time information from local weather stations, satellite imagery, cameras, and sensor networks; Enhanced forecasting for more efficient management of conventional generators; Cost reduction of starting and shutting down units; Adapting output to changing weather conditions for optimized use of power plants |

Internet of Things (IoT)
IoT is a critical component in the climate and clean technology sectors. Sensor-based solutions reduce the need for human interaction while also creating a data-rich environment for continuous service improvement. Leveraging IoT creates a win-win situation for individuals and entrepreneurs looking to reduce costs and emissions and improve their bottom lines while staying compliant with increasingly stricter regulations.
| Smart grid management | Smart wireless utility meters and real-time power monitoring; Energy-efficient homes: circuit-level electricity monitoring, real-time reporting, smart alerts, and remote energy controls; Smart lighting, heating, and cooling systems, and time-reducing energy consumption |
| Air quality monitoring | Innovative IoT sensors to monitor the air quality; IoT-based air panel devices for more efficient building ventilation |
| Smart waste management | Sensor-based smart dustbins to combat waste and garbage collection issues; IoT-based approach to generating optimized routes for waste collection and disposal |
| Smart water monitoring | IoT leak detection sensors in factories or buildings; Smart plant watering for irrigation applications based on sensor data analytics; Water quality and safety monitoring on water reserves |
| Smart agriculture | Smart farming systems; Precision farming: Livestock monitoring, vehicle tracking, field observation, and inventory monitoring; Smart greenhouses; Agricultural data analytics; Agricultural drones for crop health assessment, monitoring, planting, spraying, and field analysis |
Data engineering and analytics
As the CleanTech sector expands, the importance of data science and analytics grows exponentially. Historically, energy companies faced high costs and time constraints when interpreting data and deriving insights for decision-making. However, the improvements in sensor and connectivity technology now allow for much more efficient information processing, especially with the emergence of solutions for energy conversion, storage, and management. Here’s how data science can make a difference in the clean technology fields:
| Digital twinning | Digital twins of products for better visibility into full product life cycles, digital twins of processes and services for optimized maintenance; Green material selection for sustainable manufacturing; Investigating methods to reduce energy consumption by gaining a better understanding of energy losses; Predictive analytics to determine how various changes could reduce emissions; Risk assessments to identify operational flaws that could lead to environmentally hazardous accidents |
| Data analysis and computational models | Collecting and combining data on utilization and other sensory information to determine the peaks in power usage; Improving and implementing more efficient backup facilities to reduce power waste; Estimation of when and how much fossil fuels will be required to limit their consumption and CO2 pollution |
| Other Big Data solutions | Digital asset management platforms; Data usage patterns to improve current solar panel technology’s maintenance, efficiency, and life cycle; Algorithms to foresee and predict changes in solar and wind conditions to increase the efficiency of clean energy production; Assistance in the development of predictive energy usage models; Yield and equipment maintenance optimization by employing satellite imagery and remote sensors in the oil fields; Aid in the data-driven decision-making for clean energy industry regulators |
Cloud computing
Cloud computing improves businesses by reducing infrastructure investment costs, providing unlimited storage, increasing flexibility, and improving security, efficiency, and competitiveness. By 2028, the global cloud technology market is set to grow to nearly US $1.3 trillion. Moving to the cloud is one of the sustainable software development practices that helps minimize the negative impact of IT solutions on the environment, leading to up to 84% reduction in CO2 emissions. For companies in the climate and clean technology domains, cloud software enables remote and centralized facility control and remote access to corporate assets from any device or location. Use cases include:
| Storage monitoring | Using cloud software to monitor renewable energy storage by collecting and analyzing data from remote devices |
| Remote sensing | Dataset integration from remote cloud-connected sensors on the ground, in the air, and in space to create a global framework of CO2 level observations in real-time; Pairing smartphones with cloud-connectable sensors that monitor temperature, humidity, and air pollution |
| Machine analytics | Cloud-based software for connecting and analyzing wind farms and machinery in big and remote geographic areas; Cloud-based analysis platforms that provide access to high-res satellite imagery, geospatial models, and historical and real-time data for change detection and reporting |
| Battery aggregation | AI-powered cloud-connected battery management systems for EVs; Cloud-based battery condition monitoring platforms for IoT systems |
Mobile application development
The rapid adoption of smart devices has increased demand for mobile application development across all industries, including companies working on green technology products and services. These applications facilitate better connectivity across many value chains — from field service management and energy consumption to locating the nearest recycling station and tracking CO2 impact of a plane trip — and play a significant role in promoting sustainable living choices. Examples include:
| Energy management apps | Smart energy monitoring systems; Inverter intelligent monitoring systems; Custom renewable energy management systems; Energy mobile app solutions |
| Carbon footprint monitoring apps | Carbon footprint calculators; Environment awareness apps (tree tracking, sustainability of items, etc.) |
| Waste and recycling apps | Interactive recycling handbooks; Interactive maps of places and donation centers to donate goods (clothes, furniture. etc.); Paper waste apps |
| Water utility apps | Water usage trackers; Apps for water and wastewater system operators |
| Sustainability lifestyle apps | Social help apps; Life activities & everyday habit apps to measure the environmental impact; Community awareness apps; Environmental science apps |
GreenTech: Where software solutions align with sustainability goals
Leveraging IT solutions for environmental sustainability is one of Beetroot’s top priorities and a significant part of our sustainability strategy. As we continue to evolve as a tech ecosystem and deepen our commitment to tech for good, we firmly believe that by supporting transformative projects where our clients make significant contributions to a better world, we collectively inspire a broader movement within the tech industry toward purpose-driven projects.
GreenTech is one of Beetroot’s key focus industries because of its potential to foster this type of collaboration. Having partnered with companies active in clean energy, air purifying solutions, and smart sensors for energy efficiency, we keep learning and honing our tech knowledge on several in-house R&D projects. Whether you’re looking to accelerate your sustainable product launch, scale your team, drive innovation, or explore new opportunities, we’re here to support you on your impactful journey.
Subscribe to blog updates
Get the best new articles in your inbox. Get the lastest content first.
Recent articles from our magazine
Contact Us
Find out how we can help extend your tech team for sustainable growth.