AI Chatbots and Virtual Assistants in Green Tech: Tools for Smart Sustainability
Contents
Contents
Intro: Making Sustainability More Actionable with AI
From climate action chatbots supporting organizations with carbon tracking and reporting to promoting energy transitions, AI chatbots and virtual green assistants are quickly carving out a niche in GreenTech development. For CTOs, sustainability leaders, and digital product owners, these technologies offer scalable, intelligent ways to optimize operations and advance sustainability goals.
For this article, we shortlisted some real-world examples of AI chatbots and similar solutions in environmental sustainability, from ESG reporting and energy management to smart agriculture, urban development, and beyond.
We’ll also discuss the challenges tied to AI development, including hidden energy costs, data limitations, and privacy risks. Can AI become “greener”? We’ll look at possible ways to mitigate negative impacts and make the most of AI’s potential in the long run. Let’s dive in.
Strategic Role of AI Chatbots in Green Technology and Eco-Awareness
In May of last year, a McKinsey report found that the number of organizations that use generative AI had almost doubled to 65% in just the past ten months. In another study by IBM, 77% of respondents admitted that they needed to adopt generative AI quickly to keep up with customers.
As our world becomes increasingly interconnected and environmentally conscious, the demand for smarter solutions is growing. AI’s capacity to process vast environmental data, identify patterns, predict outcomes, and suggest interventions plays a critical role in green technology.
Enter AI chatbots — a field where the capabilities of AI truly shine, showcasing its strengths in natural language processing (NLP), machine learning, and automation. Generative AI further enhances the intelligence, adaptability, and conversational abilities of AI chatbots, making them more versatile and effective tools for a wide range of applications.
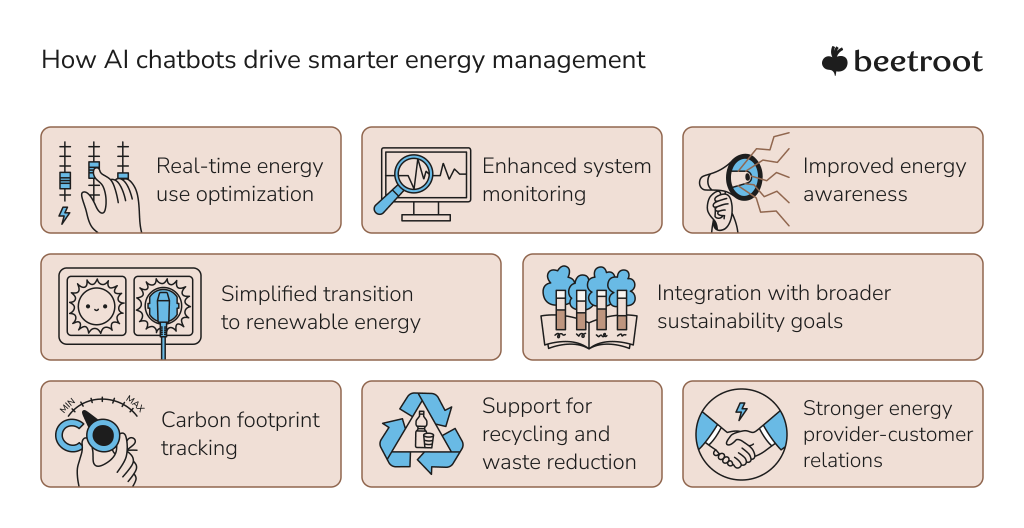
Facilitating Smart Resource Management
AI chatbots transform our approach to energy and resource efficiency. Clean energy users can benefit from AI-powered forecasts of solar power generation based on weather conditions, recommendations for optimal energy usage or storage, and detection of inefficiencies. Real-time environmental data analysis, coupled with intelligent energy solutions, helps bridge the gap between complex AI systems and actionable insights that improve renewable energy management.
The role of chatbots in smart energy systems extends to handling inquiries about energy plans, assisting with transitions to greener energy sources, and enhancing customer service quality for energy providers. In some cases, AI-driven initiatives, like East Lansing’s use of garbage trucks with AI cameras, have considerably improved recycling practices, reducing contamination rates.
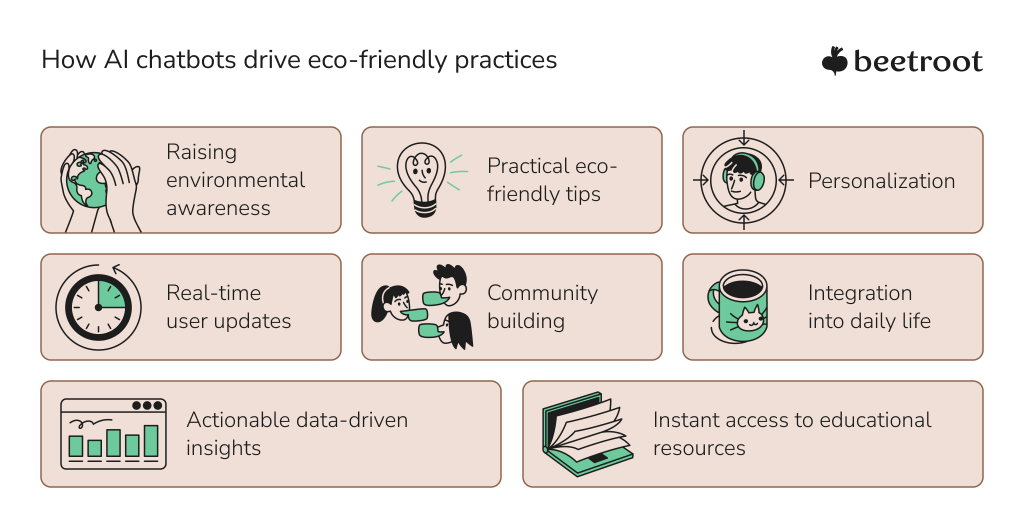
Promoting Eco-Friendly Practices
AI chatbots serve as personal virtual guides that help users adopt greener habits in their daily lives. They deliver real-time updates on environmental trends, discoveries, and developments, keeping users informed and engaged. More than just sharing information, these chatbots inspire action by encouraging participation in sustainability campaigns and promoting advocacy for environmental change.
By breaking down barriers often associated with sustainable practices, AI chatbots make eco-friendly choices more accessible. Their 24/7 availability and vast knowledge base empower users to make informed decisions, driving positive change in their communities and for the planet.
Simplifying Sustainability Reporting
AI chatbots are increasingly useful in sustainability reporting, especially in high-stakes industries like energy and manufacturing, where ESG goals are paramount. AI tools streamline data collection and analysis, offering accurate insights into a company’s environmental impact. By tracking changes in legislation, they guide teams through regulatory requirements, and ensure adherence to both local and global standards; this allows companies to share clear, transparent metrics and meet the expectations of investors, regulators, and consumers.
AI and Sustainability: Are Chatbots Eco-Friendly?
While chatbots offer sustainability benefits, they come with a carbon cost. Here’s how to evaluate and reduce their environmental impact using Green AI practices.
The Hidden Energy Cost of AI Chatbot Use
Creating an AI chatbot requires extensive computational power to train machine learning models: each interaction involves accessing data, processing user queries, and generating responses. Research from MIT highlights that training a single AI model can emit as much CO₂ as five cars over their entire lifetimes. When multiplied by billions of daily interactions across various industries, the cumulative energy impact becomes staggering.
Data Centers: The Backbone of AI Operations
The infrastructure supporting AI chatbots, primarily data centers, plays a central role in the global digital ecosystem. The most recent Deloitte analysis predicts that further adoption of AI will fuel data center power demand, potentially reaching 2,000 TWh by 2050 and accounting for 3% of global consumption.
Strategies to Minimize AI’s Carbon Footprint
Reducing the environmental impact of AI chatbots requires a proactive approach that incorporates several best practices:
- Optimize AI algorithms: Streamline AI models to lower their energy demands without sacrificing performance. Energy-efficient models are especially crucial for high-usage applications.
- Choose green hosting and server options: Hosting AI systems on data centers powered by renewable energy can significantly cut emissions. Consider eco-friendly service providers like Krystal, GreenGeeks, or Hetzner to meet your hosting needs and sustainability goals.
- Adopt edge computing: Shifting some AI processes to local servers or devices reduces reliance on cloud data centers, leading to energy savings.
- Invest in carbon offsetting: Companies can participate in initiatives that fund renewable energy projects or reforestation efforts to balance out their carbon output.
- Leverage Green AI principles: Sustainable AI chatbots align with the broader concept of Green AI, which focuses on minimizing environmental costs through smarter algorithmic design, hardware efficiency, and optimizing the operations of data centers. Unlike Green by AI, which uses AI to address global sustainability challenges like energy efficiency or climate change, Green AI directly targets the ecological footprint of AI itself. By emphasizing sustainable training and deployment, Green AI promotes a more responsible use of the technology, which is closely linked to the development of sustainable apps.
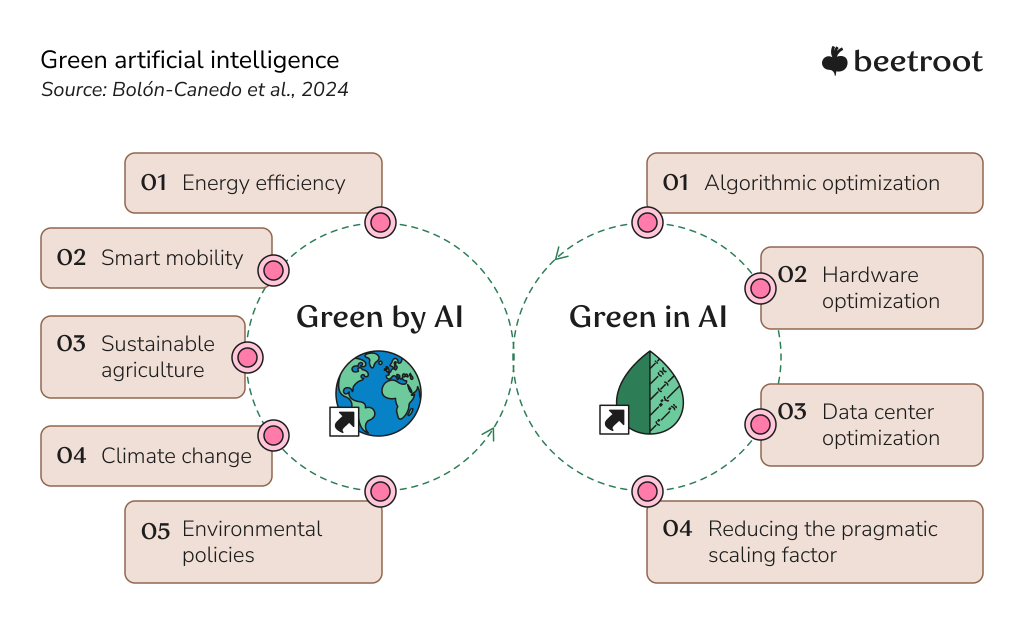
In our journey with AI, we recognize its power to drive progress toward the UN Sustainable Development Goals. However, it’s equally important to stay mindful of its environmental footprint, ensuring a balanced approach to impact-driven tech. To explore more about leveraging AI in green technology and mobile applications, check out Beetroot’s dedicated guide.
Sustainable Chatbots in Action: Fighting Greenwashing and Enabling Change
From tracking net-zero commitments to leveraging AI, NLP, and ML algorithms to optimize farming, urban design, and city planning, the chatbot use cases below showcase how AI can enhance decision-making in various sectors.
How Chatbots Detect Greenwashing & “Red Flags” in Climate Commitments
Greenwashing refers to an act of making misleading or unsubstantiated claims about a product, service, or company’s environmental benefits to appear more eco-friendly than they truly are. It can take different forms:
- Greencrowding — a tactic to dilute or obscure individual environmental accountability by blending into a group of peers or relying on collective action to avoid discovery.
- Greenlighting — advertising a green feature or sustainable initiative to overshadow or distract from an organization’s broader, less eco-friendly actions.
- Greenshifting — shifting the responsibility onto others, such as customers, employees, or other stakeholders, instead of taking accountability as an organization or entity.
- Greenlabelling — describing something as green and eco-friendly when, in reality, it’s not.
- Greenrinsing — repeatedly revising or diluting sustainability goals and presenting the adjusted targets as progress without striving to meet the original, ambitious targets.
- Greenhushing — the act of hiding or underreporting sustainability efforts to avoid scrutiny or criticism.
The risks of greenwashing include financial institutions investing in projects that appear sustainable but turn out otherwise, jeopardizing investor stability, disrupting the economy, and eroding trust in financial markets, not to mention the deception of clients. As corporate greenwashing grows more sophisticated, AI emerges as a valuable tool for detecting its traces.
ChatNetZero
ChatNetZero is the world’s first climate target chatbot designed to determine the credibility of net zero goals pledged by governments and companies. The tool uses specially trained LLMs on a live database tracking thousands of public decarbonization targets to demystify climate commitments. The bot is developed and led by an international consortium of scientists from the Data-Driven EnviroLab, Arboretica, and the Net Zero Tracker, with funding from the IKEA Foundation.

ChatReport
This web application was designed to automate the analysis of corporate sustainability reports through interactive chat interfaces. CSR reports are crucial in assessing organizations’ social and environmental impacts and risks. Developed by a group of scientists from the universities of Zurich, Oxford, and Nuremberg, ChatReport uses OpenAI’s GPT-3.5 and GPT-4 models to analyze and benchmark CSR reports against the Task Force for Climate-Related Financial Disclosures (TCFD) recommendations.
The WWF AI tool
Also co-developed with the universities of Zurich and Oxford, this AI model acts as the first screening tool to “red flag” possible instances of greenwashing in climate-related pledges, allowing authorities and investors to quickly single out companies whose plans do not seem credible for a more in-depth inspection. It follows the structure of ChatReport and is rooted in climate science based on the reports produced by the UN’s Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change (IPCC).
AI Assistants Powering the Energy Sector
Advanced chat interfaces serve as a tool for faster data querying and reporting in energy systems, one of the most challenging and demanding industries. The most promising applications of AI in the energy sector include:
Enhancing Customer Service
Using AI in customer support changes how energy companies interact with consumers, as tools like ChatGPT can handle complex queries and deliver personalized responses. AI can handle high support demand, boost agent efficiency, and enhance customer satisfaction.
Octopus Energy
UK-based energy provider Octopus Energy has pioneered the use of Generative AI to answer client emails, becoming able to process 50,000 inquiries per day. AI-generated responses received an 85% customer satisfaction rating, surpassing the human-written ones that only got a 65% score. Their proprietary energy tech platform, Kraken, uses advanced AI and ML algorithms to streamline customer operations and facilitate customer self-service and grid innovation.
Automating Routine Tasks
In addition to personalization, GenAI tools can automate much of the energy supply chain operations, support complex decision-making for energy suppliers and end customers, and free up time and human resources to perform more strategic tasks.
Ontario Power Generation
This Canadian electricity generation company launched an AI chatbot in collaboration with Microsoft to improve employee productivity and optimize internal operations. A tool called “ChatOPG” leverages NLP for real-time assistance on various internal operations — from HR processes to IT troubleshooting, acting as a personal virtual assistant for teams.

Carbon Emissions Tracking
KPMG Generative AI survey revealed that 43% of ENRC companies’ executives consider applying it for environmental monitoring and management. By connecting with comprehensive sustainability databases like Ecoinvent, AI tools help users trace the impacts of their products across supply chains and make informed decisions to take action.
Williams Companies
One of the largest energy companies in the world has partnered with Context Labs to leverage AI and blockchain technology for a granular view of their environmental impact. This approach allows Williams to enhance transparency in reporting and implement targeted emissions reduction strategies.
Renewable Energy Management
53% of ENRC executives anticipate using GenAI for renewable energy development and management. AI-powered virtual assistants are increasingly being utilized to analyze energy consumption patterns, predict equipment failures, and provide recommendations to optimize energy distribution.
SmartHelio
A Switzerland-based startup, SmartHelio, is building a proprietary “SolarGPT,” a prompt-based LLM agent similar to AI platforms like ChatGPT. The tool links to SmartHelio’s databases to provide detailed reports on PV plant operation and even support plant repowering strategies to help developers maximize the performance of their solar power units.

Predictive Maintenance
Energy providers manage complex operations and vast asset bases — no surprise they are increasingly adopting AI-powered chatbots and virtual assistants for predictive analytics. 73% of executives see GenAI’s potential for this area in their companies.
General Electric (GE)
GE uses an AI-driven predictive maintenance system that monitors the health of turbines and other critical infrastructure. This system analyzes sensor data in real-time to predict potential failures and schedule maintenance. The implementation of this AI system has significantly reduced GE’s unplanned downtime and maintenance costs.
AI Assistants in Agriculture and Horticulture
With the added capabilities of generative AI, agricultural companies could harvest new insights and better data to manage natural resources, such as soil, seed, and water. AI-powered agriculture chatbots leverage AI, NLP, and ML to assist farmers and agribusinesses in areas like crop management, weather forecasting, pest and disease identification, and market conjuncture. Examples include:
Digital Green
Digital Green, a global organization dedicated to supporting small-scale farmers worldwide through technology, has developed an AI-powered chatbot for Telegram. It improves communication between farmers and agricultural extension agents and ensures farmers can access timely, localized guidance. Looking ahead, Digital Green’s AI assistant aims to integrate local market data, including supply costs and selling prices, to provide even more comprehensive support.
Datamars
A Swiss company, Datamars, focuses on developing hardware and software technology for smart farming. They created industry-leading livestock monitoring software that helps farmers track the behavior and individual characteristics of each animal on-farm and through the cloud. It’s also available on mobile devices.
KissanAI
KissanAI is an Indian GenAI platform for agriculture. It provides a voice-enabled, multilingual virtual assistant for farmers that leverages GPT and Whisper models to provide expert agricultural, financial, and legal advice. The company is also developing Dhenu, a set of language models, and AgriCopilot — a comprehensive GenAI knowledge platform designed specifically for the agriculture industry.

GrowBot
GrowBot, the extended feature of a popular gardening app, From Seed to Spoon, provides gardeners with AI-powered knowledge and gardening advice for all experience levels. The chatbot uses advanced AI to address a wide range of topics, from pest identification to garden planning and planting dates.

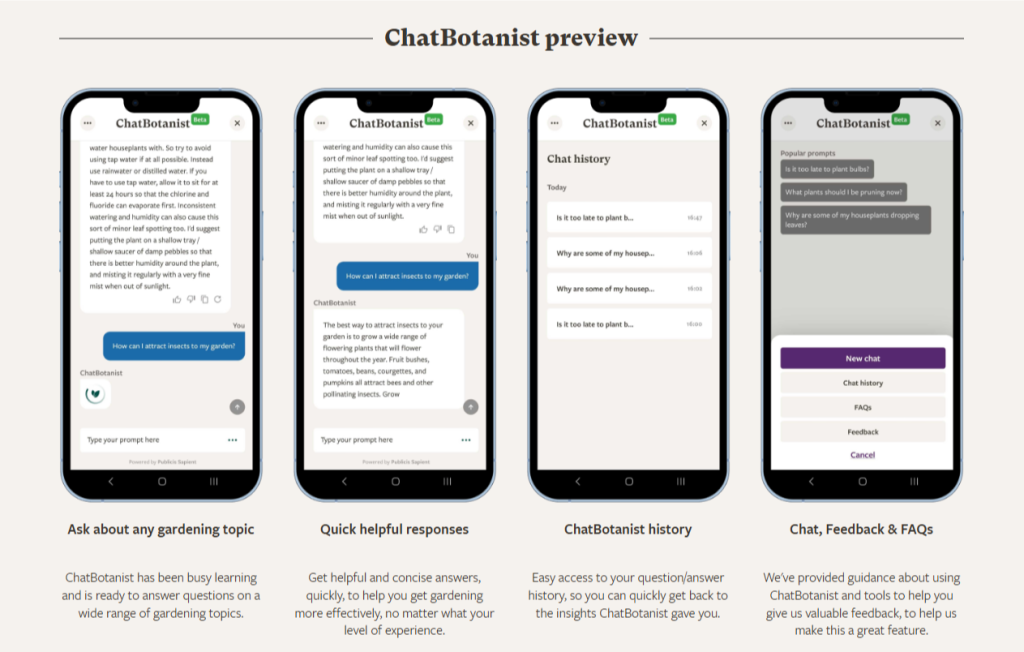
ChatBotanist
The Royal Horticultural Society (RHS) of the UK has launched an AI chatbot connected to a knowledge base developed from the insights of RHS experts. ChatBotanist can answer questions on various gardening topics, give quick and helpful responses, save users’ query history, and extend the existing services provided by RHS’s customer service team.
Urban Planning and Smart City Chatbots
AI-powered chatbots and virtual assistants help with data analysis, decision-making, and stakeholder collaboration in urban design and development. Furthermore, AI models can be valuable in identifying potential weaknesses in designs or technical problems, suggesting improvements, and supporting architects on their creative journey.
UrbanistAI
UrbanistAI uses collective intelligence and AI to ideate new concepts for public spaces and buildings. It helps evaluate design solutions and improves participatory planning and co-design, supporting dialogue between citizens and policymakers. UrbanistAI has been implemented in various cities, including Zurich, within initiatives such as Denk Züri Neu to reimagine public spaces and foster community engagement in urban planning.

BOTI
Buenos Aires, Argentina’s capital, launched its first citizen-focused chatbot on WhatsApp in 2019, which now has evolved alongside GenAI. Having served as an official government channel during the pandemic, it achieved 11 million conversations by 2022 and now includes services like social care and bike sharing.
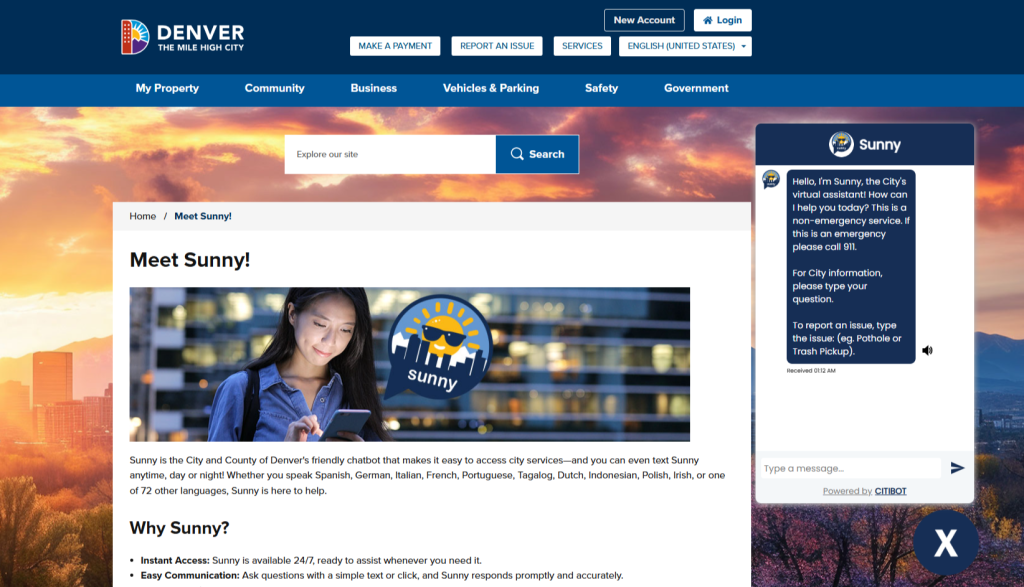
Sunny
Denver (Colorado, the US) introduced its official AI chatbot, Sunny, in February 2024. Powered by Citibot, a GenAI solutions provider and hosted on AWS, Sunny stands out from most AI bots by connecting exclusively to a proprietary local database. It offers quick access to information about city services and resources, including events, meetings, parking, trash collection, and more — all available in 72 languages.
Case Study: Building a Tailored AI Chatbot to Elevate Customer Engagement
Beetroot designed an AI-powered virtual assistant for a TravelTech company (confidential due to NDA), showcasing a scalable and adaptable architecture that can extend to other sectors, including GreenTech. Hosted on AWS ECS, the tool leverages PostgreSQL for database management and Redis for caching, with Terraform ensuring secure and consistent infrastructure deployments.
By integrating advanced NLP and a robust backend built on Django and Celery, an AI assistant can help drive sustainability by providing real-time data, personalized recommendations, and continuous engagement. This makes it a valuable tool for promoting and achieving environmental goals.
Explore our other GreenTech cases to discover how Beetroot drives sustainable software development through innovative solutions.
Overcoming Common Challenges of AI Integration in Green Tech Software Solutions
AI-powered systems in GreenTech face technical, regulatory, and operational barriers. These are the top risks and how to navigate them.
High Initial Costs
Developing and deploying AI chatbots involves a significant upfront investment, which can be a barrier for smaller organizations. The complexity of an AI model can account for 30-40% of the total project budget, with data collection and preparation being another major cost. To ease the financial strain, organizations can start small by focusing on specific use cases like waste management or carbon tracking. This incremental approach, paired with other cost-saving strategies, makes it easier to manage costs and scale over time.
AI’s Growing Energy Demand
The International Energy Agency predicts that integrating AI into tools like search engines could increase electricity demand tenfold by 2030. The industry is exploring solutions such as power-efficient hardware, smaller task-specific models, smarter training methods, and sourcing clean, renewable energy to balance technological innovation with sustainability goals.
Energy Data Inconsistency Across Sources
Another challenging factor is that energy data comes in many different formats and from various sources. For example, to address solar energy challenges and provide reliable insights to energy providers, AI has to be compatible with real-time data on generation, consumption, and weather conditions collected by IoT devices. Data inaccuracy or incompleteness can compromise the quality of AI outcomes.
LLM Incompatibility with Sensor Data
Large language models (LLMs) are primarily designed and trained to process textual information, while sensor data from energy systems is often presented in formats like numerical or time-series data. Existing models need to be adapted to address this mismatch, or new models like Archetype AI must be developed to ensure accurate and effective use in energy-related applications.
Data Privacy & Compliance
Users often have limited control over their data when interacting with chatbots, with little visibility into how their information is used, shared, or stored; this heightens privacy concerns, especially in GreenTech applications that handle sensitive environmental and business data. To address these risks, AI chatbot developers should implement data encryption, access controls, and other security methods, conduct regular vulnerability assessments, and ensure compliance with key data privacy regulations like GDPR and CCPA.
Despite these challenges, the right combination of incremental scaling, energy efficiency practices, and strong cybersecurity measures ensures that AI chatbots remain viable and impactful tools for the GreenTech industry.
The Road Ahead: AI’s Role in Achieving Net Zero
While energy consumption in large-scale data centers remains a concern, AI is increasingly recognized as a key tool in combating climate change. Sustainability experts and policymakers agree that it allows humans to prioritize carbon emission reduction and identify climate risks far more accurately than ever before. Global revenue from AI-related infrastructure, services, and analytics is forecast to reach nearly $16 trillion by 2030.
The role of AI chatbots in achieving these goals is expanding as industries integrate them with technologies like IoT, blockchain, and advanced analytics. In sustainable supply chain management, AI chatbots serve as centralized hubs for instant updates, bridging communication gaps and facilitating decision-making. They assist with monitoring sustainability metrics, prioritizing suppliers based on Scope 3 emissions, tracking compliance, and assessing material emissions. Effective implementation, however, requires active stakeholder engagement. Providing training and addressing concerns about AI’s impact on workflows is key to achieving both leadership buy-in and user acceptance.
Beetroot is a trusted partner for businesses seeking robust tech expertise and a deep understanding of their industries. Committed to advancing sustainability, we deliver tailored green software solutions, support team augmentation, and foster domain knowledge development through expert-led training in emerging technologies like GenAI, green coding, and cybersecurity. Reach out to us anytime to discuss how our expertise aligns with your goals.
FAQs About AI Chatbots in GreenTech
What are some common applications of AI chatbots in green tech and sustainability?
AI chatbots have a range of uses in sustainability. They can help optimize energy usage by analyzing data and even forecasting renewable energy production (for example, predicting solar power availability to advise when to use or store energy).
They also serve as virtual “green assistants” for people, providing real-time tips and updates on environmental topics and encouraging greener habits and actions. In organizations, chatbots can assist with tracking carbon footprints, answering sustainability questions for customers or employees, and simplifying tasks like recycling guidance or energy-saving recommendations.
How do we choose the right AI chatbot or virtual assistant for our sustainability initiatives?
While generative AI adoption is skyrocketing (77% of companies in one survey felt pressure to adopt it quickly), it’s important to pick a solution that fits your goals. Start by defining what you need the chatbot to do. Is it customer-facing to answer green product questions, an internal tool for analyzing sustainability data, or something else? Then evaluate options based on their capabilities and fit: some chatbots are general-purpose (using powerful language models) while others are tailored to specific domains like energy or climate.
Also consider practical factors like integration (can it connect with your existing data and platforms?) and the provider’s credibility and values (for example, do they prioritize data security and eco-friendly practices, which might align with your sustainability goals).
Can we integrate an AI chatbot into our existing green tech systems or processes?
Most AI chatbot platforms offer APIs or integration tools that make it fairly straightforward to embed them into your existing software, websites, or even IoT systems. You’ll likely connect the chatbot to your relevant data sources, for instance, linking it with sensor databases or sustainability data streams so it can deliver context-aware insights (like reading energy sensor data to give real-time efficiency tips).
Integration should involve your IT team to ensure the chatbot can access data securely and appear where users need it (whether that’s a web portal, a messaging app, or an internal dashboard).
How can we minimize the environmental impact of using AI chatbots?
There are several strategies to make AI chatbots greener. One approach is to improve the technology’s efficiency itself: developers can optimize AI models and algorithms so they require less computational power, and use edge computing (handling some processing on local devices or servers) to reduce reliance on energy-hungry cloud data centers.
Designing and operating AI systems with energy efficiency and minimal waste in mind helps outweigh (or balance) your chatbot’s benefits for sustainability over its carbon footprint.
Another approach is to run the chatbot on sustainable infrastructure, for example, choosing cloud or hosting providers that rely on renewable energy, and to scale resources up or down to avoid waste. Many providers also invest in carbon offsets to compensate for the emissions their AI usage does generate.
Can AI chatbots help with sustainability reporting and carbon tracking?
Absolutely. AI chatbots can support carbon tracking and sustainability reporting by pulling data such as energy use or emissions figures from connected systems and assisting in estimating an organization’s environmental footprint.
Specialized chatbots like climate target assistants can help verify the credibility of net-zero pledges, automate the review of corporate sustainability reports, and flag potential greenwashing in climate-related claims. They can also track changes in legislation and guide teams through ESG compliance, making it easier to produce transparent, audit-ready reports for stakeholders.
In more advanced setups, AI chatbots can integrate with sustainability databases (e.g., Ecoinvent) to trace product-level emissions across supply chains and highlight opportunities for reduction.
Subscribe to blog updates
Get the best new articles in your inbox. Get the lastest content first.
Recent articles from our magazine
Contact Us
Find out how we can help extend your tech team for sustainable growth.