Green UX Explained: The New Black in Clean Energy Tech
Contents
Contents
Clean energy technology offers a crucial alternative to fossil fuels in the global push for sustainability, helping reduce our carbon footprint. However, the digital technologies supporting this sector can inadvertently contribute to increased energy consumption. The emissions from the ICT sector are projected to reach 14% of the global emissions by 2040, for the most part coming from the operations of data centers and communication networks.
It’s especially relevant for AI systems, where the existing approaches to deploying and managing AI remain widely disproportionate. Advanced technologies have a tremendous potential to address complex technological challenges and improve sustainability. However, these very technologies are, paradoxically, contributing to excess energy usage and environmental inequity. For instance, when one of Google’s data centers in Finland operated on 97% renewable power in 2022, this number dropped to 4-18% for data centers located in Asia.
One answer to this paradox lies in an emerging practice known as green UX. Green UX is a design approach intended to minimize the environmental impact of digital products while maintaining functionality and user satisfaction. Green UX practices focus on energy efficiency, sustainable performance, and eco-conscious design. This article explores how green UX is emerging as the new “black” in clean energy tech, balancing user needs with environmental sustainability.
What is green UI/UX?
Green UI/UX applies to the design of user interfaces (UI) and experiences (UX) that prioritize sustainability and minimize environmental impact. While traditional UX focuses on creating intuitive, user-friendly products that reflect business goals, green UX goes a step further, promoting careful consideration of resource efficiency, performance optimization, and mindful design choices.
Design plays a crucial role in sustainability, with over 80% of all product-related environmental impacts being determined during the design phase. In essence, green UI/UX ensures that digital products reduce their negative footprint by minimizing energy consumption, data processing, and hardware strain. It asks designers and developers to be mindful of how their decisions—whether related to color palettes, data handling, or app functionality—impact the environment.
The dual approach of green UI/UX breaks down into:
- Sustainable UI: Designing visually appealing interfaces that require less battery power to display, using eco-friendly colors (yes, it is a real thing), typography, and graphics.
- Sustainable UX: Creating user experiences that optimize interactions, reduce data transfer, and inspire users to make sustainable choices.

Best practices for green UX: A holistic approach
Green UX really challenges designers to examine the design and development process through an environmental lens. As a holistic methodology, green UX aims to minimize the carbon footprint of digital products throughout their lifecycle, from concept to launch and beyond. By integrating principles of efficiency, sustainability, and usability at every stage, green UX creates a backbone of eco-conscious software design.
Best practices in sustainable UX design
Establish operational foundations for positive impact
To create truly impactful green digital products, ensure your design team includes experienced and motivated designers and developers. Encourage them to ask critical questions like: How can we streamline our processes? How can we reduce server requests, load times, and other energy-intensive operations? By focusing on positive impact, you’ll create products that are not only user-friendly but also more environmentally sustainable, benefiting both your stakeholders and the planet.
Optimize design processes
Refine your workflows to reduce operational inefficiencies between the design and development teams. Adopt a well-structured design system and leverage frameworks such as the Lightning Design System to improve collaboration between teams and ensure continuous updates and enhancements of your apps. These frameworks help streamline communication between designers and developers, reducing operational inefficiencies and enabling faster delivery of sustainable products.
Create a design system with a pattern library
Start with a well-documented style guide to ensure consistency and efficiency across all digital touchpoints. This approach simplifies the wireframing process by allowing designers to pull from a predefined library of components, eliminating unnecessary rework. It reduces design waste while ensuring that each new feature or interface element is optimized for both performance and sustainability.
Use default system fonts
When it comes to font selection, default system fonts are the most efficient choice. They reduce the number of HTTP requests required to load a page, making them significantly more efficient than embedded or custom fonts. Limit your design to a maximum of two fonts optimized for screen use.
Use low-energy color palettes
Your choice of a color palette on your website, app, or other digital media can save energy, especially on OLED screens. By utilizing low-energy colors—such as muted greens, dark grays, blues, and earthy tones—you can create visually engaging designs and balance branding, color psychology, energy efficiency, and accessibility. Consider reserving white and brighter hues for accents, ensuring that the majority of the interface conserves power without sacrificing aesthetics.
Mobile-first and responsive design
Designing with a mobile-first mindset is essential for both sustainability and user experience. Prioritize content and features essential for users with small screens or low bandwidth. Mobile devices, especially older ones, often have limited processing power and battery life, and a well-optimized mobile experience reduces the strain on these devices. The less content is to be displayed, the fewer data requests will be sent to the server, reducing its load and ultimately contributing to lower energy consumption.
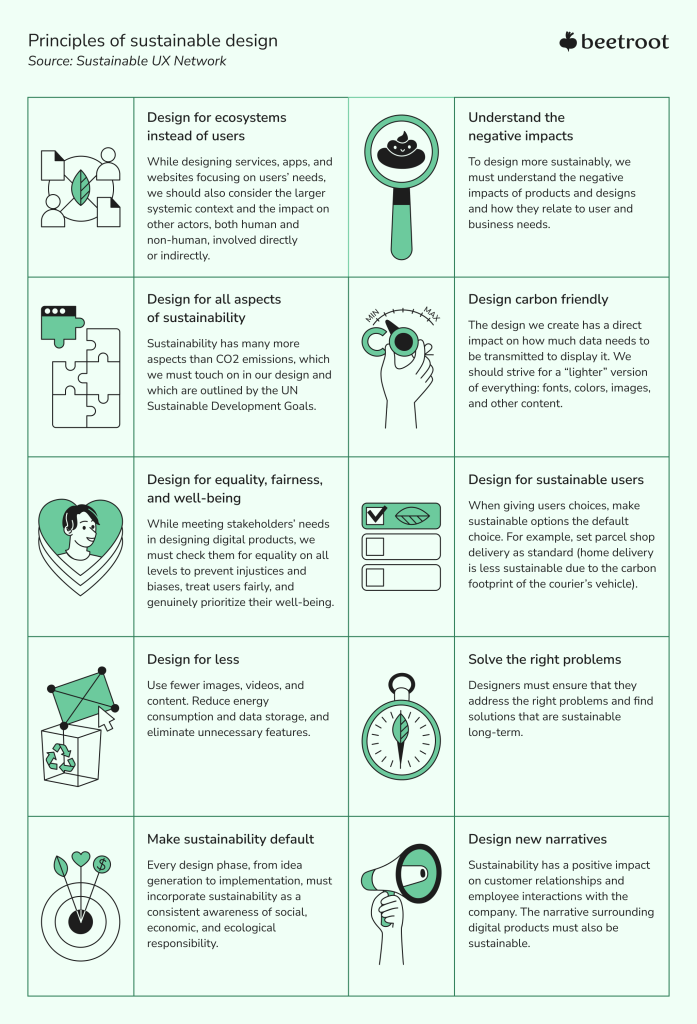
The above best practices align with the Sustainable UX Network’s principles of sustainable design, which emphasize creating something with the larger ecosystem in mind, understanding the negative impacts of products and designs, and addressing other aspects of sustainability in the process that are outlined in the UN SDGs. These principles can serve as a framework for integrating sustainability into every phase of digital product design.
Green UX implementation examples in clean energy apps
The best practices of green design are especially relevant for the clean energy sector, where apps are crafted to help users monitor and reduce their energy consumption, track real-time energy generation, integrate with utility accounts to monitor consumption and costs, and provide tools to control and optimize renewable energy systems. These apps serve as prime examples of how green UX principles can enhance functionality while reducing environmental impact. Key examples include:
Data visualization dashboards
One of the most crucial elements of clean energy apps is the ability to present complex data, such as energy usage or CO2 footprint tracking, in a user-friendly way. Energy-themed apps often use lightweight visualizations that are simple yet instructive, enabling users to make informed decisions without overloading their devices. For example, an app tracking solar energy production might display interactive graphs that update in real-time while consuming minimal processing power.
Energy-efficient color themes
Many clean energy apps utilize dark or low-energy themes to reduce screen brightness and conserve battery life on mobile devices. As we explained above, this small design choice can have a considerable impact, especially on devices with OLED screens, where dark pixels require less energy to display.
Minimalistic interfaces
Minimalistic design follows the principle of “less is more,” prioritizing essential content and functionality to avoid cognitive overload. It includes readable and elegant typography, icon-based interactions, limited or monochromatic color palettes, and simplified navigation. Clean energy apps often focus on essential functions while eliminating unnecessary features that consume additional resources. For example, a smart home energy app might provide simple controls for adjusting heating or lighting, using less screen space and requiring fewer interactions.
Progressive feature loading
Rather than loading all features and content at once and to optimize performance, many clean energy apps leverage progressive loading. It means that content is loaded as needed, reducing the strain on servers and users’ devices. This approach demonstrates how thoughtful feature implementation can support sustainability goals. For instance, an app may only activate certain energy-saving tips or suggestions when a user reaches a specific milestone, thereby reducing data usage.
Gamification and feedback loops
Many clean energy apps incorporate gamification to encourage users to engage in sustainable behaviors in an interactive, rewarding manner. For example, users might receive badges or rewards for reducing energy consumption or lowering their carbon footprint. This approach not only enhances user experience but also promotes eco-friendly actions, creating a positive cycle of engagement and environmental awareness.

The future of Green UX: a vision for CleanTech and beyond
The ecological and social responsibility that goes into green UI/UX design are inherently parts of the same processes that drive sustainable software development. By merging design practices and sustainable principles, designers and development teams pave the way for a more eco-friendly digital future. For companies looking to succeed in the clean energy tech sector and other impactful domains, green UX is no longer a trend. It’s a necessary feature that allows their products to enhance user engagement, meet regulatory demands, and contribute to the well-being of our planet.
At Beetroot, we recognize the power of technology and eco-conscious design choices in developing products that are functional and promote sustainability. Our expert design teams carefully consider every design choice, ensuring that each product and solution scenario is tailored to balance the needs of stakeholders and end users while aligning with high-level sustainability goals. Think we might be the right fit for your upcoming green or clean energy project? Share your vision with us, and let’s explore how our expertise can help bring your ideas to life.
Subscribe to blog updates
Get the best new articles in your inbox. Get the lastest content first.
Recent articles from our magazine
Contact Us
Find out how we can help extend your tech team for sustainable growth.